Multiplexed RNA structure characterization with selective 2'-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension sequencing (SHAPE-Seq)
- PMID: 21642531
- PMCID: PMC3131332
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1106501108
Multiplexed RNA structure characterization with selective 2'-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension sequencing (SHAPE-Seq)
Abstract
New regulatory roles continue to emerge for both natural and engineered noncoding RNAs, many of which have specific secondary and tertiary structures essential to their function. Thus there is a growing need to develop technologies that enable rapid characterization of structural features within complex RNA populations. We have developed a high-throughput technique, SHAPE-Seq, that can simultaneously measure quantitative, single nucleotide-resolution secondary and tertiary structural information for hundreds of RNA molecules of arbitrary sequence. SHAPE-Seq combines selective 2'-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE) chemistry with multiplexed paired-end deep sequencing of primer extension products. This generates millions of sequencing reads, which are then analyzed using a fully automated data analysis pipeline, based on a rigorous maximum likelihood model of the SHAPE-Seq experiment. We demonstrate the ability of SHAPE-Seq to accurately infer secondary and tertiary structural information, detect subtle conformational changes due to single nucleotide point mutations, and simultaneously measure the structures of a complex pool of different RNA molecules. SHAPE-Seq thus represents a powerful step toward making the study of RNA secondary and tertiary structures high throughput and accessible to a wide array of scientific pursuits, from fundamental biological investigations to engineering RNA for synthetic biological systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
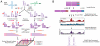
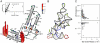
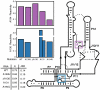

Comment in
-
RNA structure probing dash seq.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 5;108(27):10933-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107835108. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21700884 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

