Mass spectrometry-based proteomics using Q Exactive, a high-performance benchtop quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometer
- PMID: 21642640
- PMCID: PMC3284220
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M111.011015
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics using Q Exactive, a high-performance benchtop quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometer
Abstract
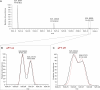
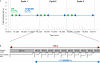
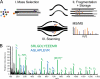
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics has greatly benefitted from enormous advances in high resolution instrumentation in recent years. In particular, the combination of a linear ion trap with the Orbitrap analyzer has proven to be a popular instrument configuration. Complementing this hybrid trap-trap instrument, as well as the standalone Orbitrap analyzer termed Exactive, we here present coupling of a quadrupole mass filter to an Orbitrap analyzer. This "Q Exactive" instrument features high ion currents because of an S-lens, and fast high-energy collision-induced dissociation peptide fragmentation because of parallel filling and detection modes. The image current from the detector is processed by an "enhanced Fourier Transformation" algorithm, doubling mass spectrometric resolution. Together with almost instantaneous isolation and fragmentation, the instrument achieves overall cycle times of 1 s for a top 10 higher energy collisional dissociation method. More than 2500 proteins can be identified in standard 90-min gradients of tryptic digests of mammalian cell lysate- a significant improvement over previous Orbitrap mass spectrometers. Furthermore, the quadrupole Orbitrap analyzer combination enables multiplexed operation at the MS and tandem MS levels. This is demonstrated in a multiplexed single ion monitoring mode, in which the quadrupole rapidly switches among different narrow mass ranges that are analyzed in a single composite MS spectrum. Similarly, the quadrupole allows fragmentation of different precursor masses in rapid succession, followed by joint analysis of the higher energy collisional dissociation fragment ions in the Orbitrap analyzer. High performance in a robust benchtop format together with the ability to perform complex multiplexed scan modes make the Q Exactive an exciting new instrument for the proteomics and general analytical communities.
Figures




References
-
- Aebersold R., Mann M. (2003) Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422, 198–207 - PubMed
-
- Yates J. R., 3rd, Gilchrist A., Howell K. E., Bergeron J. J. (2005) Proteomics of organelles and large cellular structures. Nat. Rev. 6, 702–714 - PubMed
-
- Michalski A., Cox J., Mann M. (2011) More than 100,000 Detectable Peptide Species Elute in Single Shotgun Proteomics Runs but the Majority is Inaccessible to Data-Dependent LC-MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 10, 1785–1793 - PubMed
-
- Köcher T., Swart R., Mechtler K. (2011) Ultra-High-Pressure RPLC Hyphenated to an LTQ-Orbitrap Velos Reveals a Linear Relation between Peak Capacity and Number of Identified Peptides. Anal. Chem. 83, 2699–2704 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

