Structure-function studies of FMRP RGG peptide recognition of an RNA duplex-quadruplex junction
- PMID: 21642970
- PMCID: PMC3130835
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2064
Structure-function studies of FMRP RGG peptide recognition of an RNA duplex-quadruplex junction
Abstract
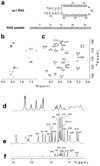
We have determined the solution structure of the complex between an arginine-glycine-rich RGG peptide from the human fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) and an in vitro-selected guanine-rich (G-rich) sc1 RNA. The bound RNA forms a newly discovered G-quadruplex separated from the flanking duplex stem by a mixed junctional tetrad. The RGG peptide is positioned along the major groove of the RNA duplex, with the G-quadruplex forcing a sharp turn of R(10)GGGGR(15) at the duplex-quadruplex junction. Arg10 and Arg15 form cross-strand specificity-determining intermolecular hydrogen bonds with the major-groove edges of guanines of adjacent Watson-Crick G•C pairs. Filter-binding assays on RNA and peptide mutations identify and validate contributions of peptide-RNA intermolecular contacts and shape complementarity to molecular recognition. These findings on FMRP RGG domain recognition by a combination of G-quadruplex and surrounding RNA sequences have implications for the recognition of other genomic G-rich RNAs.
Figures






References
-
- Saxena S, Miyoshi D, Sugimoto N. Sole and stable RNA duplexes of G-rich sequences located in the 5'-untranslated region of protooncogenes. Biochemistry. 2010;49:7190–7201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

