Phosphorylation and interaction of myopodin by integrin-link kinase lead to suppression of cell growth and motility in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 21643011
- PMCID: PMC3170684
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.200
Phosphorylation and interaction of myopodin by integrin-link kinase lead to suppression of cell growth and motility in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
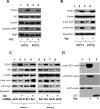
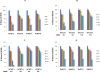
Myopodin is a tumor-suppressor gene that suppresses growth of prostate and urothelial carcinomas. However, the mechanism of myopodin tumor-suppressor activity or signaling that leads to activation of myopodin remains unclear. In this report, we showed that the N-terminus of myopodin binds integrin-linked kinase (ILK) both in vivo and in vitro. An ILK interaction motif of 78 amino acids (amino acids 82-157) was identified in the N-terminus region of myopodin. Induction of ILK-dependent kinase activity by integrin α7 led to phosphorylation of myopodin both in vivo and in vitro. Knocking down ILK dramatically reduced the inhibition of cell growth and motility mediated by myopodin. A mutant of myopodin lacking the ILK interaction motif is inactive in suppressing the growth and motility of PC3 cells. As a result, this study showed a novel and critical signaling pathway that leads to activation of myopodin.
Figures


References
-
- Cebrian V, Alvarez M, Aleman A, Palou J, Bellmunt J, Gonzalez-Peramato P, et al. Discovery of myopodin methylation in bladder cancer. J Pathol. 2008;216:111–9. - PubMed
-
- Deng JT, Van Lierop JE, Sutherland C, Walsh MP. Ca2+-independent smooth muscle contraction. a novel function for integrin-linked kinase. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:16365–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

