The metabolic advantage of tumor cells
- PMID: 21649891
- PMCID: PMC3118193
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-70
The metabolic advantage of tumor cells
Abstract
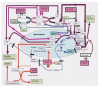
1- Oncogenes express proteins of "Tyrosine kinase receptor pathways", a receptor family including insulin or IGF-Growth Hormone receptors. Other oncogenes alter the PP2A phosphatase brake over these kinases. 2- Experiments on pancreatectomized animals; treated with pure insulin or total pancreatic extracts, showed that choline in the extract, preserved them from hepatomas. Since choline is a methyle donor, and since methylation regulates PP2A, the choline protection may result from PP2A methylation, which then attenuates kinases. 3- Moreover, kinases activated by the boosted signaling pathway inactivate pyruvate kinase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. In addition, demethylated PP2A would no longer dephosphorylate these enzymes. A "bottleneck" between glycolysis and the oxidative-citrate cycle interrupts the glycolytic pyruvate supply now provided via proteolysis and alanine transamination. This pyruvate forms lactate (Warburg effect) and NAD+ for glycolysis. Lipolysis and fatty acids provide acetyl CoA; the citrate condensation increases, unusual oxaloacetate sources are available. ATP citrate lyase follows, supporting aberrant transaminations with glutaminolysis and tumor lipogenesis. Truncated urea cycles, increased polyamine synthesis, consume the methyl donor SAM favoring carcinogenesis. 4- The decrease of butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, elicits epigenic changes (PETEN, P53, IGFBP decrease; hexokinase, fetal-genes-M2, increase). 5- IGFBP stops binding the IGF - IGFR complex, it is perhaps no longer inherited by a single mitotic daughter cell; leading to two daughter cells with a mitotic capability. 6- An excess of IGF induces a decrease of the major histocompatibility complex MHC1, Natural killer lymphocytes should eliminate such cells that start the tumor, unless the fever prostaglandin PGE2 or inflammation, inhibit them...
Figures
References
-
- Mazurek S, Eigenbrodt E. The tumor metabolome. Anticancer Res. 2003;23(2A):1149–54. - PubMed
-
- Hitosugi T, Kang S, Vander Heiden MG, Chung TW, Elf S, Lythgoe K, Dong S, Lonial S, Wang X, Cheng GZ, Xie J, Gu TL, Polakiewicz RD, Roesel JL, Boggon TJ, Khuri FR, Gilliland DG, Cantley LC, Kaufman J, Cheng J. Tyrosine Phosphorylation inhibits PKM2 to promote the Warburg effect and tumor growth. Sci Signal. 2009;2(97):l–8. ra73. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

