De novo sequence assembly and characterization of the floral transcriptome in cross- and self-fertilizing plants
- PMID: 21649902
- PMCID: PMC3128866
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-298
De novo sequence assembly and characterization of the floral transcriptome in cross- and self-fertilizing plants
Abstract
Background: The shift from cross-fertilization to predominant self-fertilization is among the most common evolutionary transitions in the reproductive biology of flowering plants. Increased inbreeding has important consequences for floral morphology, population genetic structure and genome evolution. The transition to selfing is usually characterized by a marked reduction in flower size and the loss of traits involved in pollinator attraction and the avoidance of self-fertilization. Here, we use short-read sequencing to assemble, de novo, the floral transcriptomes of three genotypes of Eichhornia paniculata, including an outcrosser and two genotypes from independently derived selfers, and a single genotype of the sister species E. paradoxa. By sequencing mRNA from tissues sampled at various stages of flower development, our goal was to sequence and assemble the floral transcriptome and identify differential patterns of gene expression.
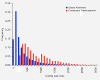
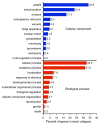
Results: Our 24 Mbp assembly resulted in ~27,000 contigs that averaged ~900 bp in length. All four genotypes had highly correlated gene expression, but the three E. paniculata genotypes were more correlated with one another than each was to E. paradoxa. Our analysis identified 269 genes associated with floral development, 22 of which were differentially expressed in selfing lineages relative to the outcrosser. Many of the differentially expressed genes affect floral traits commonly altered in selfing plants and these represent a set of potential candidate genes for investigating the evolution of the selfing syndrome.
Conclusions: Our study is among the first to demonstrate the use of Illumina short read sequencing for de novo transcriptome assembly in non-model species, and the first to implement this technology for comparing floral transcriptomes in outcrossing and selfing plants.
Figures


References
-
- Stebbins GL. Flowering Plants Evolution Above the Species Level. Cambridge, MA: Belkknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1974.
-
- Baker HG. Self-compatibility and establishment after "long distance" dispersal. Evolution. 1955;9:347–348. doi: 10.2307/2405656. - DOI
-
- Lloyd DG. Evolution of self-compatibility and racial differentiation in Leavenworthia (Cruciferae) Contributions from the Gray Herbarium of Harvard University. 1965;195:3–134.
-
- Ornduff R. Reproductive biology in relation to systematics. Taxon. 1969;18:121–133. doi: 10.2307/1218671. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

