A laminopathic mutation disrupting lamin filament assembly causes disease-like phenotypes in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 21653823
- PMCID: PMC3145547
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-01-0064
A laminopathic mutation disrupting lamin filament assembly causes disease-like phenotypes in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
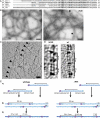
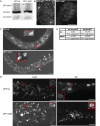
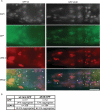
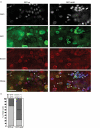
Mutations in the human LMNA gene underlie many laminopathic diseases, including Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD); however, a mechanistic link between the effect of mutations on lamin filament assembly and disease phenotypes has not been established. We studied the ΔK46 Caenorhabditis elegans lamin mutant, corresponding to EDMD-linked ΔK32 in human lamins A and C. Cryo-electron tomography of lamin ΔK46 filaments in vitro revealed alterations in the lateral assembly of dimeric head-to-tail polymers, which causes abnormal organization of tetrameric protofilaments. Green fluorescent protein (GFP):ΔK46 lamin expressed in C. elegans was found in nuclear aggregates in postembryonic stages along with LEM-2. GFP:ΔK46 also caused mislocalization of emerin away from the nuclear periphery, consistent with a decreased ability of purified emerin to associate with lamin ΔK46 filaments in vitro. GFP:ΔK46 animals had motility defects and muscle structure abnormalities. These results show that changes in lamin filament structure can translate into disease-like phenotypes via altering the localization of nuclear lamina proteins, and suggest a model for how the ΔK32 lamin mutation may cause EDMD in humans.
Figures


References
-
- Aebi U, Cohn J, Buhle L, Gerace L. The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature. 1986;323:560–564. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Harush K, Wiesel N, Frenkiel-Krispin D, Moeller D, Soreq E, Aebi U, Herrmann H, Gruenbaum Y, Medalia O. The supramolecular organization of the C. elegans nuclear lamin filament. J Mol Biol. 2009;386:1392–1402. - PubMed
-
- Bione S, Maestrini E, Rivella S, Mancini M, Regis S, Romeo G, Toniolo D. Identification of a novel X-linked gene responsible for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1994;8:323–327. - PubMed
-
- Bonne G, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1999;21:285–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

