Specific regulation of NRG1 isoform expression by neuronal activity
- PMID: 21653853
- PMCID: PMC3154699
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5317-10.2011
Specific regulation of NRG1 isoform expression by neuronal activity
Abstract
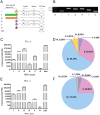
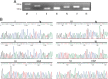
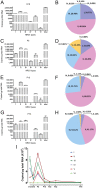
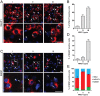
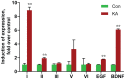
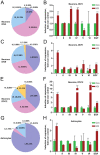
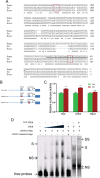
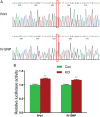
Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) is a trophic factor that has been implicated in neural development, neurotransmission, and synaptic plasticity. NRG1 has multiple isoforms that are generated by usage of different promoters and alternative splicing of a single gene. However, little is known about NRG1 isoform composition profile, whether it changes during development, or the underlying mechanisms. We found that each of the six types of NRG1 has a distinct expression pattern in the brain at different ages, resulting in a change in NRG1 isoform composition. In both human and rat, the most dominant are types III and II, followed by either type I or type V, while types IV and VI are the least abundant. The expression of NRG1 isoforms is higher in rat brains at ages of E13 and P5 (in particular type V), suggesting roles in early neural development and in the neonatal critical period. At the cellular level, the majority of NRG1 isoforms (types I, II, and III) are expressed in excitatory neurons, although they are also present in GABAergic neurons and astrocytes. Finally, the expression of each NRG1 isoform is distinctly regulated by neuronal activity, which causes significant increase in type I and IV NRG1 levels. Neuronal activity regulation of type IV expression requires a CRE cis-element in the 5' untranslated region (UTR) that binds to CREB. These results indicate that expression of NRG1 isoforms is regulated by distinct mechanisms, which may contribute to versatile functions of NRG1 and pathologic mechanisms of brain disorders such as schizophrenia.
Figures
References
-
- Anton ES, Marchionni MA, Lee KF, Rakic P. Role of GGF/neuregulin signaling in interactions between migrating neurons and radial glia in the developing cerebral cortex. Development. 1997;124:3501–3510. - PubMed
-
- Asai M, Iwasaki Y, Yoshida M, Mutsuga-Nakayama N, Arima H, Ito M, Takano K, Oiso Y. Nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) is involved in the depolarization-induced activation of growth hormone-releasing hormone gene transcription in vitro. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;18:3011–3019. - PubMed
-
- Bellocchio EE, Reimer RJ, Fremeau RT, Jr, Edwards RH. Uptake of glutamate into synaptic vesicles by an inorganic phosphate transporter. Science. 2000;289:957–960. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
