Determination of malignant and invasive predictors in branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a suggested scoring formula
- PMID: 21655058
- PMCID: PMC3102866
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.6.740
Determination of malignant and invasive predictors in branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a suggested scoring formula
Abstract
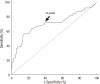
Prediction of malignancy or invasiveness of branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (Br-IPMN) is difficult, and proper treatment strategy has not been well established. The authors investigated the characteristics of Br-IPMN and explored its malignancy or invasiveness predicting factors to suggest a scoring formula for predicting pathologic results. From 1994 to 2008, 237 patients who were diagnosed as Br-IPMN at 11 tertiary referral centers in Korea were retrospectively reviewed. The patients' mean age was 63.1 ± 9.2 yr. One hundred ninty-eight (83.5%) patients had nonmalignant IPMN (81 adenoma, 117 borderline atypia), and 39 (16.5%) had malignant IPMN (13 carcinoma in situ, 26 invasive carcinoma). Cyst size and mural nodule were malignancy determining factors by multivariate analysis. Elevated CEA, cyst size and mural nodule were factors determining invasiveness by multivariate analysis. Using the regression coefficient for significant predictors on multivariate analysis, we constructed a malignancy-predicting scoring formula: 22.4 (mural nodule [0 or 1]) + 0.5 (cyst size [mm]). In invasive IPMN, the formula was expressed as invasiveness-predicting score = 36.6 (mural nodule [0 or 1]) + 32.2 (elevated serum CEA [0 or 1]) + 0.6 (cyst size [mm]). Here we present a scoring formula for prediction of malignancy or invasiveness of Br-IPMN which can be used to determine a proper treatment strategy.
Keywords: Branch Duct Type Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN); CEA; Cyst Size; Invasive Carcinoma; Malignancy; Mural Nodule.
Figures

References
-
- Longnecker DS, Adsay NV, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Hruban RH, Kasugai T, Klimstra DS, Kloppel G, Luttges J, Memoli VA, Tosteson TD, Yanagisawa A, Wilentz R, Zamboni G. Histopathological diagnosis of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms: interobserver agreement. Pancreas. 2005;31:344–349. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M, Yamaguchi K, Yamao K, Matsuno S International Association of Pancreatology. International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2006;6:17–32. - PubMed
-
- Jang JY, Kim SW, Lee SE, Yang SH, Lee KU, Lee YJ, Kim SC, Han DJ, Choi DW, Choi SH, Heo JS, Cho BH, Yu HC, Yoon DS, Lee WJ, Lee HE, Kang GH, Lee JM. Treatment guidelines for branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: when can we operate or observe? Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt CM, White PB, Waters JA, Yiannoutsos CT, Cummings OW, Baker M, Howard TJ, Zyromski NJ, Nakeeb A, DeWitt JM, Akisik FM, Sherman S, Pitt HA, Lillemoe KD. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: predictors of malignant and invasive pathology. Ann Surg. 2007;246:644–651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

