GWAS for discovery and replication of genetic loci associated with sudden cardiac arrest in patients with coronary artery disease
- PMID: 21658281
- PMCID: PMC3141757
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-11-29
GWAS for discovery and replication of genetic loci associated with sudden cardiac arrest in patients with coronary artery disease
Abstract
Background: Epidemiologic evidence suggests a heritable component to risk for sudden cardiac arrest independent of risk for myocardial infarction. Recent candidate gene association studies for community sudden cardiac arrests have focused on a limited number of biological pathways and yielded conflicting results. We sought to identify novel gene associations for sudden cardiac arrest in patients with coronary artery disease by performing a genome-wide association study.
Methods: Tagging SNPs (n = 338,328) spanning the genome were typed in a case-control study comparing 89 patients with coronary artery disease and sudden cardiac arrest due to ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation to 520 healthy controls.
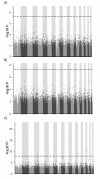
Results: Fourteen SNPs including 7 SNPs among 7 genes (ACYP2, AP1G2, ESR1, DGES2, GRIA1, KCTD1, ZNF385B) were associated with sudden cardiac arrest (all p < 1.30 × 10(-7)), following Bonferroni correction and adjustment for population substructure, age, and sex; genetic variation in ESR1 (p = 2.62 × 10(-8); Odds Ratio [OR] = 1.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]:1.277, 1.596) has previously been established as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. In tandem, the role of 9 genes for monogenic long QT syndrome (LQT1-9) was assessed, yielding evidence of association with CACNA1C (LQT8; p = 3.09 × 10(-4); OR = 1.18, 95% CI:1.079, 1.290). We also assessed 4 recently published gene associations for sudden cardiac arrest, validating NOS1AP (p = 4.50 × 10(-2), OR = 1.15, 95% CI:1.003, 1.326), CSMD2 (p = 6.6 × 10(-3), OR = 2.27, 95% CI:1.681, 2.859), and AGTR1 (p = 3.00 × 10(-3), OR = 1.13, 95% CI:1.042, 1.215).
Conclusion: We demonstrate 11 gene associations for sudden cardiac arrest due to ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation in patients with coronary artery disease. Validation studies in independent cohorts and functional studies are required to confirm these associations.
Figures
References
-
- Zipes DP, Wellens HJ. Sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 1998;98:2334–2351. - PubMed
-
- Dekker LR, Bezzina CR, Henriques JP, Tanck MW, Koch KT, Alings MW, Arnold AE, de Boer MJ, Gorgels AP, Michels HR. et al.Familial sudden death is an important risk factor for primary ventricular fibrillation: a case-control study in acute myocardial infarction patients. Circulation. 2006;114:1140–1145. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.606145. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous