Rare de novo variants associated with autism implicate a large functional network of genes involved in formation and function of synapses
- PMID: 21658583
- PMCID: PMC3607702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.021
Rare de novo variants associated with autism implicate a large functional network of genes involved in formation and function of synapses
Abstract
Identification of complex molecular networks underlying common human phenotypes is a major challenge of modern genetics. In this study, we develop a method for network-based analysis of genetic associations (NETBAG). We use NETBAG to identify a large biological network of genes affected by rare de novo CNVs in autism. The genes forming the network are primarily related to synapse development, axon targeting, and neuron motility. The identified network is strongly related to genes previously implicated in autism and intellectual disability phenotypes. Our results are also consistent with the hypothesis that significantly stronger functional perturbations are required to trigger the autistic phenotype in females compared to males. Overall, the presented analysis of de novo variants supports the hypothesis that perturbed synaptogenesis is at the heart of autism. More generally, our study provides proof of the principle that networks underlying complex human phenotypes can be identified by a network-based functional analysis of rare genetic variants.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

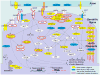
Comment in
-
Solving the autism puzzle a few pieces at a time.Neuron. 2011 Jun 9;70(5):806-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.025. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 21658575
-
Autism: The importance of getting the dose right.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011 Jul 20;12(8):429. doi: 10.1038/nrn3083. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21772319 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alvarez VA, Sabatini BL. Anatomical and physiological plasticity of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:79–97. - PubMed
-
- Blanchoin L, Pollard TD, Mullins RD. Interactions of ADF/cofilin, Arp2/3 complex, capping protein and profilin in remodeling of branched actin filament networks. Curr Biol. 2000;10:1273–1282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

