Estimation of RF energy absorbed in the brain from mobile phones in the Interphone Study
- PMID: 21659468
- PMCID: PMC3158331
- DOI: 10.1136/oemed-2011-100065
Estimation of RF energy absorbed in the brain from mobile phones in the Interphone Study
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to develop an estimate of a radio frequency (RF) dose as the amount of mobile phone RF energy absorbed at the location of a brain tumour, for use in the Interphone Epidemiological Study.
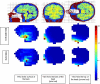
Methods: We systematically evaluated and quantified all the main parameters thought to influence the amount of specific RF energy absorbed in the brain from mobile telephone use. For this, we identified the likely important determinants of RF specific energy absorption rate during protocol and questionnaire design, we collected information from study subjects, network operators and laboratories involved in specific energy absorption rate measurements and we studied potential modifiers of phone output through the use of software-modified phones. Data collected were analysed to assess the relative importance of the different factors, leading to the development of an algorithm to evaluate the total cumulative specific RF energy (in joules per kilogram), or dose, absorbed at a particular location in the brain. This algorithm was applied to Interphone Study subjects in five countries.
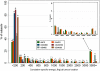
Results: The main determinants of total cumulative specific RF energy from mobile phones were communication system and frequency band, location in the brain and amount and duration of mobile phone use. Though there was substantial agreement between categorisation of subjects by cumulative specific RF energy and cumulative call time, misclassification was non-negligible, particularly at higher frequency bands. Factors such as adaptive power control (except in Code Division Multiple Access networks), discontinuous transmission and conditions of phone use were found to have a relatively minor influence on total cumulative specific RF energy.
Conclusions: While amount and duration of use are important determinants of RF dose in the brain, their impact can be substantially modified by communication system, frequency band and location in the brain. It is important to take these into account in analyses of risk of brain tumours from RF exposure from mobile phones.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Interphone, IARC and radiofrequency fields: where to next?Occup Environ Med. 2011 Sep;68(9):629-30. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2011-100358. Occup Environ Med. 2011. PMID: 21835976 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cardis E, Richardson L, Deltour I, et al. The INTERPHONE study: design, epidemiological methods, and description of the study population. Eur J Epidemiol 2007;22:647–64 - PubMed
-
- Dreyer NA, Loughlin JE, Rothman KJ. Cause-specific mortality in cellular telephone users. JAMA 1999;282:1814–16 - PubMed
-
- Johansen C, Boice J, Jr, McLaughlin J, et al. Cellular telephones and cancer–a nationwide cohort study in Denmark. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001;93:203–7 - PubMed
-
- Schüz J, Jacobsen R, Olsen JH, et al. Cellular telephone use and cancer risk: update of a nationwide Danish cohort. J Natl Cancer Inst 2006;98:1707–13 - PubMed
-
- Auvinen A, Hietanen M, Luukkonen R, et al. Brain tumors and salivary gland cancers among cellular telephone users. Epidemiology 2002;13:356–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
