The roles of lipid oxidation products and receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB signaling in atherosclerotic calcification
- PMID: 21659652
- PMCID: PMC3128471
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234245
The roles of lipid oxidation products and receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB signaling in atherosclerotic calcification
Abstract
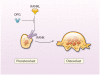
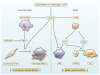
This review focuses on the roles of oxylipids and receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand signaling in calcific cardiovascular disease. Both intimal and valvular calcifications are closely associated with atherosclerosis, leading investigators to study the role of atherogenic oxidatively modified lipids (oxylipids). Results have identified the molecular signaling through which oxylipids induce osteogenic differentiation and calcification in vascular cells. A surprising concomitant finding was that, in bona fide osteoblasts from skeletal bone, oxylipids have the opposite effect, ie, inhibiting osteoblastic maturation. This is the basis for the lipid hypothesis of osteoporosis. Oxylipids also induce resorptive osteoclastic cells within the bone environment, raising the question of whether resorptive osteoclasts can be harnessed in the vascular context for cell-based therapy to remove artery wall mineral deposits. The challenge is that vascular cells produce antiosteoclastogenic factors, including the soluble decoy receptor for receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, possibly accounting for the paucity of resorptive cells and the dominance of mineral in atherosclerotic plaque. These factors may have therapeutic use in osteoclastogenic removal of mineral deposits from arteries.
Figures

References
-
- Bolland MJ, Wang TK, van Pelt NC, Horne AM, Mason BH, Ames RW, Grey AB, Ruygrok PN, Gamble GD, Reid IR. Abdominal aortic calcification on vertebral morphometry images predicts incident myocardial infarction. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25:505–512. - PubMed
-
- Proudfoot D, Davies JD, Skepper JN, Weissberg PL, Shanahan CM. Acetylated low-density lipoprotein stimulates human vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by promoting osteoblastic differentiation and inhibiting phagocytosis. Circulation. 2002;106:3044–3050. - PubMed
-
- Tanimura A, McGregor DH, Anderson HC. Matrix vesicles in atherosclerotic calcification. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983;172:173–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

