Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors attenuate neuroinflammation following focal cerebral ischemia in mice
- PMID: 21660152
- PMCID: PMC3104200
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.2.115
Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors attenuate neuroinflammation following focal cerebral ischemia in mice
Abstract
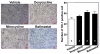
The aim of this study was to investigate whether matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitors attenuate neuroinflammation in an ischemic brain following photothrombotic cortical ischemia in mice. Male C57BL/6 mice were anesthetized, and Rose Bengal was systemically administered. Permanent focal ischemia was induced in the medial frontal and somatosensory cortices by irradiating the skull with cold white light. MMP inhibitors, such as doxycycline, minocycline, and batimastat, significantly reduced the cerebral infarct size, and the expressions of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). However, they had no effect on the expressions of heme oxygenase-1 and neuroglobin in the ischemic cortex. These results suggest that MMP inhibitors attenuate ischemic brain injury by decreasing the expression levels of MCP-1, TNF-α, and IDO, thereby providing a therapeutic benefit against cerebral ischemia.
Keywords: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor; Monocyte chemotactic protein-1; Photothrombotic cortical ischemia; Tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures





References
-
- Denes A, Thornton P, Rothwell NJ, Allan SM. Inflammation and brain injury: acute cerebral ischaemia, peripheral and central inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2010;24:708–723. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation. Glia. 2002;39:279–291. - PubMed
-
- Mun-Bryce S, Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinases in cerebrovascular disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998;18:1163–1172. - PubMed
-
- Asahi M, Asahi K, Jung JC, del Zoppo GJ, Fini ME, Lo EH. Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal cerebral ischemia: effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition with BB-94. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:1681–1689. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

