Cytokeratin-19 mRNA-positive circulating tumor cells during follow-up of patients with operable breast cancer: prognostic relevance for late relapse
- PMID: 21663668
- PMCID: PMC3218949
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2897
Cytokeratin-19 mRNA-positive circulating tumor cells during follow-up of patients with operable breast cancer: prognostic relevance for late relapse
Abstract
Background: The detection of cytokeratin-19 (CK-19) mRNA-positive circulating tumor cells (CTC) before and/or after adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with operable breast cancer is associated with poor clinical outcome. Reliable prognostic markers for late disease relapse are not available. In this study we investigated the value of CTC detection during the first five years of follow-up in predicting late disease relapse.
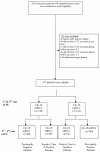
Methods: Blood was analyzed from 312 women with operable breast cancer who had not experienced disease relapse during the first two years of follow-up. A real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for CK-19 mRNA was used to detect CTC three months after the completion of adjuvant chemotherapy and every six months thereafter for a follow-up period of five years.
Results: Eighty patients (25.6% of the study population) remained CTC free throughout the five-year period. A change in CTC status was observed in 133 patients (42.6%); 64 patients (20.5%) with initially CK-19 mRNA-positive CTC during the first 24 months turned CTC-negative afterwards while 69 (22.1%) who were initially CTC-negative became CTC-positive. Ninety-nine patients (31.7%) remained persistently CK-19 mRNA-positive. After a median follow-up period of 107 months (range: 38 to 161 months), the persistently CTC-positive patients with either hormonal receptor positive or negative tumors, had a higher risk of late-disease relapse compared to the persistently CTC-negative patients (36.4% versus 11.2%, P <0.001). Multivariate analysis revealed that persistently CTC-positive patients also had a shorter disease-free (P = 0.001) and overall survival (P = 0.001).
Conclusions: Persistent detection of CK-19 mRNA-positive CTC during the first five years of follow-up is associated with an increased risk of late relapse and death in patients with operable breast cancer and indicates the presence of chemo-and hormonotherapy-resistant residual disease. This prognostic evaluation may be useful when deciding on subsequent adjuvant systemic therapy.
Figures
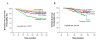

Similar articles
-
Detection of circulating cytokeratin-19 mRNA-positive cells in the blood and the mitotic index of the primary tumor have independent prognostic value in early breast cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2014 Dec;14(6):442-50. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Clin Breast Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24958324
-
Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer Patients Using Cytokeratin-19 Real-Time RT-PCR.Yonsei Med J. 2017 Jan;58(1):19-26. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.1.19. Yonsei Med J. 2017. PMID: 27873491 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of cytokeratin 19, human mammaglobin, and carcinoembryonic antigen-positive circulating tumor cells by three-marker reverse transcription-PCR assay and its relation to clinical outcome in early breast cancer.Int J Biol Markers. 2010 Apr-Jun;25(2):59-68. doi: 10.1177/172460081002500201. Int J Biol Markers. 2010. PMID: 20586026
-
CTCs in primary breast cancer (II).Recent Results Cancer Res. 2012;195:187-92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-28160-0_17. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22527506 Review.
-
Clinical challenges in the molecular characterization of circulating tumour cells in breast cancer.Br J Cancer. 2013 Jun 25;108(12):2426-32. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.265. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23756869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of cancer before distant metastasis.BMC Cancer. 2013 Jun 13;13:283. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-283. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23763955 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating tumor cells in non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Sep;147(2):325-33. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3103-7. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014. PMID: 25164970 Free PMC article.
-
TTF-1- and/or CD56-positive Circulating Tumor Cells in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC).Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 28;7:45351. doi: 10.1038/srep45351. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28349943 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic characterization of circulating tumor cells in the peripheral blood of patients with small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 18;12(7):e0181211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181211. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28719656 Free PMC article.
-
Keratin 19 regulates cell cycle pathway and sensitivity of breast cancer cells to CDK inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 10;9(1):14650. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51195-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31601969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, Fryback DG, Clarke L, Zelen M, Mandelblatt JS, Yakovlev AY, Habbema JD, Feuer EJ. Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) Collaborators. Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1784–1792. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050518. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosen PP, Groshen S, Kinne DW. Prognosis in T2N0M0 stage I breast carcinoma: a 20-year follow-up study. J Clin Oncol. 1991;9:1650–1661. - PubMed
-
- Saphner T, Tormey DC, Gray R. Annual hazard rates of recurrence for breast cancer after primary therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:2738–2746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

