The RNA helicase Mtr4p modulates polyadenylation in the TRAMP complex
- PMID: 21663793
- PMCID: PMC3115544
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.010
The RNA helicase Mtr4p modulates polyadenylation in the TRAMP complex
Abstract
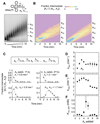
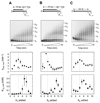
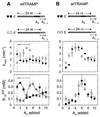
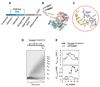
Many steps in nuclear RNA processing, surveillance, and degradation require TRAMP, a complex containing the poly(A) polymerase Trf4p, the Zn-knuckle protein Air2p, and the RNA helicase Mtr4p. TRAMP polyadenylates RNAs designated for decay or trimming by the nuclear exosome. It has been unclear how polyadenylation by TRAMP differs from polyadenylation by conventional poly(A) polymerase, which produces poly(A) tails that stabilize RNAs. Using reconstituted S. cerevisiae TRAMP, we show that TRAMP inherently suppresses poly(A) addition after only 3-4 adenosines. This poly(A) tail length restriction is controlled by Mtr4p. The helicase detects the number of 3'-terminal adenosines and, over several adenylation steps, elicits precisely tuned adjustments of ATP affinities and rate constants for adenylation and TRAMP dissociation. Our data establish Mtr4p as a critical regulator of polyadenylation by TRAMP and reveal that an RNA helicase can control the activity of another enzyme in a highly complex fashion and in response to features in RNA.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Ali JA, Lohman TM. Kinetic measurement of the step size of DNA unwinding by Escherichia coli UvrD helicase. Science. 1997;275:377–380. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JT, Wang X. Nuclear RNA surveillance: no sign of substrates tailing off. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;44:16–24. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein J, Patterson DN, Wilson GM, Toth EA. Characterization of the essential activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mtr4p, a 3'–>5' helicase partner of the nuclear exosome. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:4930–4942. - PubMed
-
- Bonneau F, Basquin J, Ebert J, Lorentzen E, Conti E. The yeast exosome functions as a macromolecular cage to channel RNA substrates for degradation. Cell. 2009;139:547–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

