Riboneogenesis in yeast
- PMID: 21663798
- PMCID: PMC3163394
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.022
Riboneogenesis in yeast
Abstract
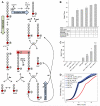
Glucose is catabolized in yeast via two fundamental routes, glycolysis and the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, which produces NADPH and the essential nucleotide component ribose-5-phosphate. Here, we describe riboneogenesis, a thermodynamically driven pathway that converts glycolytic intermediates into ribose-5-phosphate without production of NADPH. Riboneogenesis begins with synthesis, by the combined action of transketolase and aldolase, of the seven-carbon bisphosphorylated sugar sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate. In the pathway's committed step, sedoheptulose bisphosphate is hydrolyzed to sedoheptulose-7-phosphate by the enzyme sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase (SHB17), whose activity we identified based on metabolomic analysis of the corresponding knockout strain. The crystal structure of Shb17 in complex with sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate reveals that the substrate binds in the closed furan form in the active site. Sedoheptulose-7-phosphate is ultimately converted by known enzymes of the nonoxidative pentose phosphate pathway to ribose-5-phosphate. Flux through SHB17 increases when ribose demand is high relative to demand for NADPH, including during ribosome biogenesis in metabolically synchronized yeast cells.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
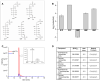
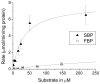
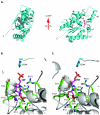
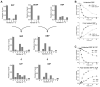

References
-
- SGD project [November 16, 2010];Saccharomyces Genome Database. http://www.yeastgenome.org/
-
- Allen J, Davey HM, Broadhurst D, Heald JK, Rowland JJ, Oliver SG, Kell DB. High-throughput classification of yeast mutants for functional genomics using metabolic footprinting. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:692–696. - PubMed
-
- Amberg DC, Burke DJ, Strathern JN. Methods in Yeast Genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2005.
-
- Bartlett GR, Bucolo G. Octulose phosphates from the human red blood cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960;3:474–478. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett GR, Bucolo G. The metabolism of ribonucleoside by the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968;156:240–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

