Controlling reaction specificity in pyridoxal phosphate enzymes
- PMID: 21664990
- PMCID: PMC3359020
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.05.019
Controlling reaction specificity in pyridoxal phosphate enzymes
Abstract
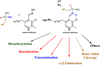
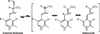
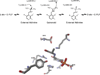
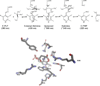
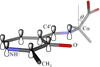
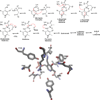
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate enzymes are ubiquitous in the nitrogen metabolism of all organisms. They catalyze a wide variety of reactions including racemization, transamination, decarboxylation, elimination, retro-aldol cleavage, Claisen condensation, and others on substrates containing an amino group, most commonly α-amino acids. The wide variety of reactions catalyzed by PLP enzymes is enabled by the ability of the covalent aldimine intermediate formed between substrate and PLP to stabilize carbanionic intermediates at Cα of the substrate. This review attempts to summarize the mechanisms by which reaction specificity can be achieved in PLP enzymes by focusing on three aspects of these reactions: stereoelectronic effects, protonation state of the external aldimine intermediate, and interaction of the carbanionic intermediate with the protein side chains present in the active site. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Pyridoxal Phosphate Enzymology.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

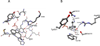

References
-
- Christen P, Metzler DE. Transaminases. New York: Wiley; 1985.
-
- John RA. Pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1248:81–96. - PubMed
-
- Toth K, Amyes TL, Richard JP, Malthouse JP, NiBeilliu ME. Claisen-type addition of glycine to pyridoxal in water. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:10538–10539. - PubMed
-
- Kerbarh O, Campopiano DJ, Baxter RL. Mechanism of alpha-oxoamine synthases: identification of the intermediate Claisen product in the 8-amino-7-oxononanoate synthase reaction. Chem Commun (Camb) 2006:60–62. - PubMed
-
- Kubota T, Shimono J, Kanameda C, Izumi Y. The first thermophilic alpha-oxoamine synthase family enzyme that has activities of 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate CoA ligase and 7-keto-8-aminopelargonic acid synthase: cloning and overexpression of the gene from an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus, and characterization of its gene product. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2007;71:3033–3040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

