Receptor tyrosine kinases and TLR/IL1Rs unexpectedly activate myeloid cell PI3kγ, a single convergent point promoting tumor inflammation and progression
- PMID: 21665146
- PMCID: PMC3144144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.04.016
Receptor tyrosine kinases and TLR/IL1Rs unexpectedly activate myeloid cell PI3kγ, a single convergent point promoting tumor inflammation and progression
Abstract
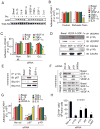
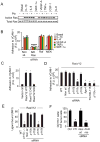
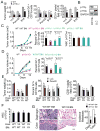
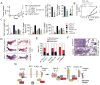
Tumor inflammation promotes angiogenesis, immunosuppression, and tumor growth, but the mechanisms controlling inflammatory cell recruitment to tumors are not well understood. We found that a range of chemoattractants activating G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and Toll-like/IL-1 receptors (TLR/IL1Rs) unexpectedly initiate tumor inflammation by activating the PI3-kinase isoform p110γ in Gr1+CD11b+ myeloid cells. Whereas GPCRs activate p110γ in a Ras/p101-dependent manner, RTKs and TLR/IL1Rs directly activate p110γ in a Ras/p87-dependent manner. Once activated, p110γ promotes inside-out activation of a single integrin, α4β1, causing myeloid cell invasion into tumors. Pharmacological or genetic blockade of p110γ suppressed inflammation, growth, and metastasis of implanted and spontaneous tumors, revealing an important therapeutic target in oncology.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
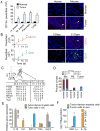
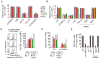
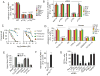
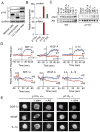
Comment in
-
A lipid kinase cousin cooperates to promote cancer.Cancer Cell. 2011 Jun 14;19(6):693-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.05.020. Cancer Cell. 2011. PMID: 21665142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnaout MA, Mahalingam B, Xiong JP. Integrin structure, allostery, and bidirectional signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:381–410. - PubMed
-
- Biswas SK, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:889–896. - PubMed
-
- Bunt SK, Sinha P, Clements VK, Leips J, Ostrand-Rosenberg S. Inflammation induces myeloid-derived suppressor cells that facilitate tumor progression. J Immunol. 2006;176:284–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01CA83133/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL31950/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA11818/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA050286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2OD004265/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA167426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AR27214/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA45726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138676/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA045726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL031950/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AR027214/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD004265/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA083133/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA126820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 CA148897/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA126820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA50286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 CA118182/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR027214/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

