Amygdala responses to averted vs direct gaze fear vary as a function of presentation speed
- PMID: 21666261
- PMCID: PMC3375890
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsr038
Amygdala responses to averted vs direct gaze fear vary as a function of presentation speed
Abstract
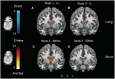
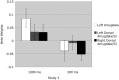
We examined whether amygdala responses to rapidly presented fear expressions are preferentially tuned to averted vs direct gaze fear and conversely whether responses to more sustained presentations are preferentially tuned to direct vs averted gaze fear. We conducted three functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies to test these predictions including: Study 1: a block design employing sustained presentations (1 s) of averted vs direct gaze fear expressions taken from the Pictures of Facial Affect; Study 2: a block design employing rapid presentations (300 ms) of these same stimuli and Study 3: a direct replication of these studies in the context of a single experiment using stimuli selected from the NimStim Emotional Face Stimuli. Together, these studies provide evidence consistent with an early, reflexive amygdala response tuned to clear threat and a later reflective response tuned to ambiguous threat.
Figures
References
-
- Adams RB, Jr, Ambady N, Macrae CN, Kleck RE. Emotional expressions forecast approach-avoidance behavior. Motivation and Emotion. 2006;30(2):177–86.
-
- Adams RB, Jr, Franklin RG., Jr Influence of emotional expression on the processing of gaze direction. Motivation and Emotion. 2009;33:106–12.
-
- Adams RB, Jr, Franklin RG, Jr, Nelson AJ, Stevenson MT. Compound social cues in face processing. In: Adams RB Jr, Ambady N, Nakayama K, Shimojo S, editors. The Science of Social Vision. New York: Oxford University Press; 2010a. pp. 90–107.
-
- Adams RB, Jr, Gordon HL, Baird AA, Ambady N, Kleck RE. Effects of gaze on amygdala sensitivity to anger and fear faces. Science. 2003;300:1536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

