Liver ischemia and reperfusion injury: new insights into mechanisms of innate-adaptive immune-mediated tissue inflammation
- PMID: 21668640
- PMCID: PMC3658307
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03579.x
Liver ischemia and reperfusion injury: new insights into mechanisms of innate-adaptive immune-mediated tissue inflammation
Abstract
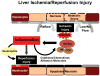
Ischemia and reperfusion injury (IRI) is a dynamic process that involves two distinctive yet interrelated phases of ischemic organ damage and inflammation-mediated reperfusion injury. Although multiple cellular and molecular pathways contribute and regulate tissue/organ damage, integration of different players into a unified mechanism is warranted. The crosstalk between innate and adaptive immune systems plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of liver IRI. In this review, we focus on recent progress in the mechanism of liver innate immune activation by IR. Kupffer cells (KC), DCs, NK, as well as T cells initiate local inflammation response, the hallmark of IRI, by utilizing distinctive immune receptors to recognize and/or trigger various molecules, both endogenous and exogenous. The interlocked molecular signaling pathways in the context of multiple liver cell types, the IRI kinetics and positive versus negative regulatory loops in the innate immune activation process are discussed. Better appreciation of molecular interactions that mediate these intricate cascades, should allow for the development of novel therapeutic approached against IRI in liver transplant recipients.
No claim to original US government works Journal compilation©2011 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose, as described by the American Journal of Transplantation.
Figures

References
-
- Fondevila C, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW. Hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury--a fresh look. Exp Mol Pathol. 2003;74(2):86–93. - PubMed
-
- Henderson JM. Liver transplantation and rejection: an overview. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 1999;46 (Suppl 2):1482–1484. - PubMed
-
- Howard TK, Klintmalm GB, Cofer JB, Husberg BS, Goldstein RM, Gonwa TA. The influence of preservation injury on rejection in the hepatic transplant recipient. Transplantation. 1990;49(1):103–107. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda T, Yanaga K, Kishikawa K, Kakizoe S, Shimada M, Sugimachi K. Ischemic injury in liver transplantation: difference in injury sites between warm and cold ischemia in rats. Hepatology. 1992;16(2):454–461. - PubMed
-
- Huet PM, Nagaoka MR, Desbiens G, Tarrab E, Brault A, Bralet MP, et al. Sinusoidal endothelial cell and hepatocyte death following cold ischemia-warm reperfusion of the rat liver. Hepatology. 2004;39(4):1110–1119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

