An integrated, multistudy analysis of the safety of Ann Arbor strain live attenuated influenza vaccine in children aged 2-17 years
- PMID: 21668683
- PMCID: PMC3256242
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2011.00243.x
An integrated, multistudy analysis of the safety of Ann Arbor strain live attenuated influenza vaccine in children aged 2-17 years
Abstract
Background: Trivalent, Ann Arbor strain, live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) is approved in several countries for use in eligible children aged ≥2 years.
Objective: To describe the safety of Ann Arbor strain LAIV in children aged 2-17 years.
Methods: An integrated analysis of randomized, controlled trials of LAIV.
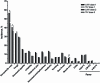
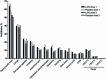
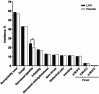
Results: A total of 4245 and 10,693 children received ≥1 dose of LAIV in year 1 of 6 trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (TIV)-controlled and 14 placebo-controlled studies, respectively; 3212 children were revaccinated in year 2 of 4 placebo-controlled studies. Compared with placebo for days 0-10 post-vaccination, LAIV recipients exhibited increased runny/stuffy nose (+7%), headache (+7%), and tiredness/decreased activity (+2%) after dose 1; and a higher rate of decreased appetite (+4%) after year 2 revaccination. Compared with TIV, only runny/stuffy nose was increased (dose 1, +12%; dose 2, +4%). Compared with initial vaccination, LAIV reactogenicity was lower after dose 2 in year 1 and revaccination in year 2. Unsolicited adverse events (AEs) increased with LAIV in some comparisons were headache, nasal congestion/rhinorrhea, rhinitis, and pyrexia; ear pain and lower respiratory illness were decreased. There was no evidence of an increase in any potential vaccine-related serious AE in LAIV recipients. Among children aged 2-17 years and specifically aged 24-35 months, there was no evidence that lower respiratory illness or wheezing illness occurred at a higher rate in LAIV recipients.
Conclusion: This analysis supports the safety of Ann Arbor strain LAIV in children aged 2-17 years and provides a consensus assessment of events expected after vaccination.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Maassab HF. Plaque formation of influenza virus at 25°C. Nature 1968; 219:645–646. - PubMed
-
- Belshe RB, Edwards KM, Vesikari T et al. Live attenuated versus inactivated influenza vaccine in infants and young children. N Engl J Med 2007; 356:685–696. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi S, Vertruyen A, Aristegui J et al. Superior relative efficacy of live attenuated influenza vaccine compared with inactivated influenza vaccine in young children with recurrent respiratory tract infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2006; 25:870–879. - PubMed
-
- Fleming DM, Crovari P, Wahn U et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of live attenuated cold‐adapted influenza vaccine, trivalent, with trivalent inactivated influenza virus vaccine in children and adolescents with asthma. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2006; 25:860–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

