Foxp3-positive macrophages display immunosuppressive properties and promote tumor growth
- PMID: 21670203
- PMCID: PMC3135357
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20100730
Foxp3-positive macrophages display immunosuppressive properties and promote tumor growth
Retraction in
-
Retraction. Foxp3-positive macrophages display immunosuppressive properties and promote tumor growth.J Exp Med. 2011 Nov 21;208(12):2561. doi: 10.1084/jem.2010073020812r. Epub 2011 Nov 14. J Exp Med. 2011. PMID: 22084411 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
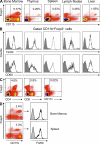
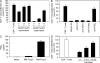
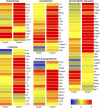
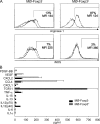
Regulatory T cells (T reg cells) are characterized by the expression of the forkhead lineage-specific transcription factor Foxp3, and their main function is to suppress T cells. While evaluating T reg cells, we identified a population of Foxp3-positive cells that were CD11b(+)F4/80(+)CD68(+), indicating macrophage origin. These cells were observed in spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, thymus, liver, and other tissues of naive animals. To characterize this subpopulation of macrophages, we devised a strategy to purify CD11b(+)F4/80(+)Foxp3(+) macrophages using Foxp3-GFP mice. Analysis of CD11b(+)F4/80(+)Foxp3(+) macrophage function indicated that these cells inhibited the proliferation of T cells, whereas Foxp3(-) macrophages did not. Suppression of T cell proliferation was mediated through soluble factors. Foxp3(-) macrophages acquired Foxp3 expression after activation, which conferred inhibitory properties that were indistinguishable from natural Foxp3(+) macrophages. The cytokine and transcriptional profiles of Foxp3(+) macrophages were distinct from those of Foxp3(-) macrophages, indicating that these cells have different biological functions. Functional in vivo analyses indicated that CD11b(+)F4/80(+)Foxp3(+) macrophages are important in tumor promotion and the induction of T reg cell conversion. For the first time, these studies demonstrate the existence of a distinct subpopulation of naturally occurring macrophage regulatory cells in which expression of Foxp3 correlates with suppressive function.
Figures





Comment in
-
Immune regulation: macrophages join the FOXP3 suppressor gang.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Jun 24;11(7):438. doi: 10.1038/nri3015. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21701515 No abstract available.
-
You, me and Foxp3: immune regulation for two.Immunotherapy. 2011 Oct;3(10):1139-42. doi: 10.2217/imt.11.118. Immunotherapy. 2011. PMID: 21995568
-
New players in immune regulation.Immunotherapy. 2011 Nov;3(11):1290-1. Immunotherapy. 2011. PMID: 22167904 No abstract available.
References
-
- Amatschek S., Lucas R., Eger A., Pflueger M., Hundsberger H., Knoll C., Grosse-Kracht S., Schuett W., Koszik F., Maurer D., Wiesner C. 2011. CXCL9 induces chemotaxis, chemorepulsion and endothelial barrier disruption through CXCR3-mediated activation of melanoma cells. Br. J. Cancer. 104:469–479 10.1038/sj.bjc.6606056 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apolloni E., Bronte V., Mazzoni A., Serafini P., Cabrelle A., Segal D.M., Young H.A., Zanovello P. 2000. Immortalized myeloid suppressor cells trigger apoptosis in antigen-activated T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 165:6723–6730 - PubMed
-
- Bacchetta R., Passerini L., Gambineri E., Dai M., Allan S.E., Perroni L., Dagna-Bricarelli F., Sartirana C., Matthes-Martin S., Lawitschka A., et al. 2006. Defective regulatory and effector T cell functions in patients with FOXP3 mutations. J. Clin. Invest. 116:1713–1722 10.1172/JCI25112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

