Galectin-9 binding to cell surface protein disulfide isomerase regulates the redox environment to enhance T-cell migration and HIV entry
- PMID: 21670307
- PMCID: PMC3127870
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1017954108
Galectin-9 binding to cell surface protein disulfide isomerase regulates the redox environment to enhance T-cell migration and HIV entry
Abstract
Interaction of cell surface glycoproteins with endogenous lectins on the cell surface regulates formation and maintenance of plasma membrane domains, clusters signaling complexes, and controls the residency time of glycoproteins on the plasma membrane. Galectin-9 is a soluble, secreted lectin that binds to glycoprotein receptors to form galectin-glycoprotein lattices on the cell surface. Whereas galectin-9 binding to specific glycoprotein receptors induces death of CD4 Th1 cells, CD4 Th2 cells are resistant to galectin-9 death due to alternative glycosylation. On Th2 cells, galectin-9 binds cell surface protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), increasing retention of PDI on the cell surface and altering the redox status at the plasma membrane. Cell surface PDI regulates integrin function on platelets and also enhances susceptibility of T cells to infection with HIV. We find that galectin-9 binding to PDI on Th2 cells results in increased cell migration through extracellular matrix via β3 integrins, identifying a unique mechanism to regulate T-cell migration. In addition, galectin-9 binding to PDI on T cells potentiates infection with HIV. We identify a mechanism for regulating cell surface redox status via a galectin-glycoprotein lattice, to regulate distinct T-cell functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

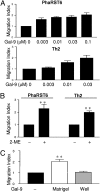

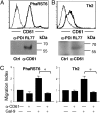
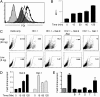
References
-
- Jordan PA, Gibbins JM. Extracellular disulfide exchange and the regulation of cellular function. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:312–324. - PubMed
-
- Hogg PJ. Disulfide bonds as switches for protein function. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:210–214. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence DA, Song R, Weber P. Surface thiols of human lymphocytes and their changes after in vitro and in vivo activation. J Leukoc Biol. 1996;60:611–618. - PubMed
-
- Turano C, Coppari S, Altieri F, Ferraro A. Proteins of the PDI family: Unpredicted non-ER locations and functions. J Cell Physiol. 2002;193:154–163. - PubMed
-
- Fenouillet E, Barbouche R, Courageot J, Miquelis R. The catalytic activity of protein disulfide isomerase is involved in human immunodeficiency virus envelope-mediated membrane fusion after CD4 cell binding. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:744–752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

