Calpain chronicle--an enzyme family under multidisciplinary characterization
- PMID: 21670566
- PMCID: PMC3153876
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.87.287
Calpain chronicle--an enzyme family under multidisciplinary characterization
Abstract
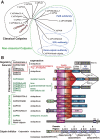
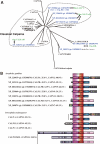
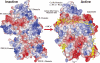
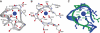
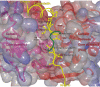
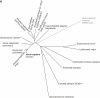
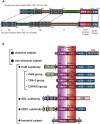
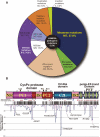
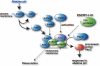
Calpain is an intracellular Ca2+-dependent cysteine protease (EC 3.4.22.17; Clan CA, family C02) discovered in 1964. It was also called CANP (Ca2+-activated neutral protease) as well as CASF, CDP, KAF, etc. until 1990. Calpains are found in almost all eukaryotes and a few bacteria, but not in archaebacteria. Calpains have a limited proteolytic activity, and function to transform or modulate their substrates' structures and activities; they are therefore called, "modulator proteases." In the human genome, 15 genes--CAPN1, CAPN2, etc.--encode a calpain-like protease domain. Their products are calpain homologs with divergent structures and various combinations of functional domains, including Ca2+-binding and microtubule-interaction domains. Genetic studies have linked calpain deficiencies to a variety of defects in many different organisms, including lethality, muscular dystrophies, gastropathy, and diabetes. This review of the study of calpains focuses especially on recent findings about their structure-function relationships. These discoveries have been greatly aided by the development of 3D structural studies and genetic models.
Figures



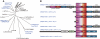






References
-
- Guroff G. (1964) A neutral calcium-activated proteinase from the soluble fraction of rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 239, 149–155 - PubMed
-
- Lazarovici P. (2000) Obituary: Dr. Gordon Guroff (1933–1999). J. Mol. Neurosci. 14, 1–2 - PubMed
-
- Huston R.B., Krebs E.G. (1968) Activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. II. Identification of the kinase activating factor as a proteolytic enzyme. Biochemistry 7, 2116–2122 - PubMed
-
- Meyer W.L., Fischer E.H., Krebs E.G. (1964) Activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. Biochemistry 3, 1033–1039 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

