mTOR complex 2 signaling and functions
- PMID: 21670596
- PMCID: PMC3322468
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.10.14.16586
mTOR complex 2 signaling and functions
Abstract
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) plays a central role in cellular growth and metabolism. mTOR forms two distinct protein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. Much is known about the regulation and functions of mTORC1 due to availability of a natural compound, rapamycin, that inhibits this complex. Studies that define mTORC2 cellular functions and signaling have lagged behind. The development of pharmacological inhibitors that block mTOR kinase activity, and thereby inhibit both mTOR complexes, along with availability of mice with genetic knockouts in mTOR complex components have now provided new insights on mTORC2 function and regulation. Since prolonged effects of rapamycin can also disrupt mTORC2, it is worth re-evaluating the contribution of this less-studied mTOR complex in cancer, metabolic disorders and aging. In this review, we focus on recent developments on mammalian mTORC2 signaling mechanisms and its cellular and tissue-specific functions.
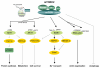
Figures


References
-
- Heitman J, Movva NR, Hall MN. Targets for cell cycle arrest by the immunosuppressant rapamycin in yeast. Science. 1991;253:905–909. - PubMed
-
- Sabatini DM, Erdjument-Bromage H, Lui M, Tempst P, Snyder SH. RAFT1: A mammalian protein that binds to FKBP12 in a rapamycin-dependent fashion and is homologous to yeast TORs. Cell. 1994;78:35–43. - PubMed
-
- Brown EJ, Albers MW, Shin TB, Ichikawa K, Keith CT, Lane WS, et al. A mammalian protein targeted by G1-arresting rapamycin-receptor complex. Nature. 1994;369:756–758. - PubMed
-
- Zheng XF, Florentino D, Chen J, Crabtree GR, Schreiber SL. TOR kinase domains are required for two distinct functions, only one of which is inhibited by rapamycin. Cell. 1995;82:121–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
