Stress and inflammation reduce brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in first-episode psychosis: a pathway to smaller hippocampal volume
- PMID: 21672499
- PMCID: PMC4082665
- DOI: 10.4088/JCP.10m06745
Stress and inflammation reduce brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in first-episode psychosis: a pathway to smaller hippocampal volume
Abstract
Background: Reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels have been reported in the serum and plasma of patients with psychosis. The aim of this cross-sectional case-control study was to investigate potential causes and consequences of reduced BDNF expression in these patients by examining the association between BDNF levels and measures of stress, inflammation, and hippocampal volume in first-episode psychosis.
Method: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, interleukin (IL)-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α messenger RNA levels were measured in the leukocytes of 49 first-episode psychosis patients (DSM-IV criteria) and 30 healthy controls, all aged 18 to 65 years, recruited between January 2006 and December 2008. Patients were recruited from inpatient and outpatient units of the South London and Maudsley National Health Service Foundation Trust in London, United Kingdom, and the healthy controls were recruited from the same catchment area via advertisement and volunteer databases. In these same subjects, we measured salivary cortisol levels and collected information about psychosocial stressors (number of childhood traumas, number of recent stressors, and perceived stress). Finally, hippocampal volume was measured using brain magnetic resonance imaging in a subsample of 19 patients.
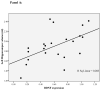
Results: Patients had reduced BDNF (effect size, d = 1.3; P < .001) and increased IL-6 (effect size, d = 1.1; P < .001) and TNF-α (effect size, d = 1.7; P < .001) gene expression levels when compared with controls, as well as higher levels of psychosocial stressors. A linear regression analysis in patients showed that a history of childhood trauma and high levels of recent stressors predicted lower BDNF expression through an inflammation-mediated pathway (adjusted R(2) = 0.23, P = .009). In turn, lower BDNF expression, increased IL-6 expression, and increased cortisol levels all significantly and independently predicted a smaller left hippocampal volume (adjusted R(2) = 0.71, P < .001).
Conclusions: Biological changes activated by stress represent a significant factor influencing brain structure and function in first-episode psychosis through an effect on BDNF.
© Copyright 2011 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Durany N, Michel T, Zochling R, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin 3 in schizophrenic psychoses. Schizophr Res. 2001;52:79–86. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda Y, Yahata N, Ito I, et al. Low serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and epidermal growth factor in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2008;101:58–66. - PubMed
-
- Rizos EN, Michalopoulou PG, Siafakas N, et al. Association of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor and duration of untreated psychosis in first-episode patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology. 2010;62:87–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

