An insect nidovirus emerging from a primary tropical rainforest
- PMID: 21673192
- PMCID: PMC3111606
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00077-11
An insect nidovirus emerging from a primary tropical rainforest
Abstract
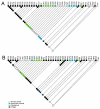
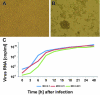
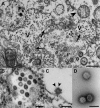
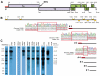
Tropical rainforests show the highest level of terrestrial biodiversity and may be an important contributor to microbial diversity. Exploitation of these ecosystems may foster the emergence of novel pathogens. We report the discovery of the first insect-associated nidovirus, tentatively named Cavally virus (CAVV). CAVV was found with a prevalence of 9.3% during a survey of mosquito-associated viruses along an anthropogenic disturbance gradient in Côte d'Ivoire. Analysis of habitat-specific virus diversity and ancestral state reconstruction demonstrated an origin of CAVV in a pristine rainforest with subsequent spread into agriculture and human settlements. Virus extension from the forest was associated with a decrease in virus diversity (P<0.01) and an increase in virus prevalence (P<0.00001). CAVV is an enveloped virus with large surface projections. The RNA genome comprises 20,108 nucleotides with seven major open reading frames (ORFs). ORF1a and -1b encode two large proteins that share essential features with phylogenetically higher representatives of the order Nidovirales, including the families Coronavirinae and Torovirinae, but also with families in a basal phylogenetic relationship, including the families Roniviridae and Arteriviridae. Genetic markers uniquely conserved in nidoviruses, such as an endoribonuclease- and helicase-associated zinc-binding domain, are conserved in CAVV. ORF2a and -2b are predicted to code for structural proteins S and N, respectively, while ORF3a and -3b encode proteins with membrane-spanning regions. CAVV produces three subgenomic mRNAs with 5' leader sequences (of different lengths) derived from the 5' end of the genome. This novel cluster of mosquito-associated nidoviruses is likely to represent a novel family within the order Nidovirales.
© 2011 Zirkel et al.
Figures
References
-
- Boesch C, Boesch-Achermann H. 2000. The chimpanzees of the Tai forest: behavioural ecology and evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford, United Kingdom
-
- Myers N. 1990. The biodiversity challenge: expanded hot-spots analysis. Environmentalist 10:243–256 - PubMed
-
- Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GA, Kent J. 2000. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 403:853–858 - PubMed
-
- Chapman CA, Balcomb SR, Gillespie TR, Skorupa JP, Struhsaker TT. 2000. Long-term effects of logging on African primate communities: a 28-year comparison from Kibale National Park, Uganda. Conserv. Biol. 14:207–217
-
- Hall JS, Harris DJ, Medjibe V, Ashton PMS. 2003. The effects of selective logging on forest structure and tree species composition in a Central African forest: implications for management of conservation areas. Forest Ecol. Manag. 183:249–264
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
