Extracellular histones promote thrombin generation through platelet-dependent mechanisms: involvement of platelet TLR2 and TLR4
- PMID: 21673343
- PMCID: PMC3158722
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-343061
Extracellular histones promote thrombin generation through platelet-dependent mechanisms: involvement of platelet TLR2 and TLR4
Abstract
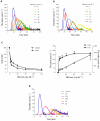
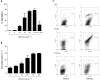
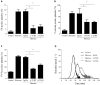
The release of histones from dying cells is associated with microvascular thrombosis and, because histones activate platelets, this could represent a possible pathogenic mechanism. In the present study, we assessed the influence of histones on the procoagulant potential of human platelets in platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and in purified systems. Histones dose-dependently enhanced thrombin generation in PRP in the absence of any trigger, as evaluated by calibrated automated thrombinography regardless of whether the contact phase was inhibited. Activation of coagulation required the presence of fully activatable platelets and was not ascribable to platelet tissue factor, whereas targeting polyphosphate with phosphatase reduced thrombin generation even when factor XII (FXII) was blocked or absent. In the presence of histones, purified polyphosphate was able to induce thrombin generation in plasma independently of FXII. In purified systems, histones induced platelet aggregation; P-selectin, phosphatidylserine, and FV/Va expression; and prothrombinase activity. Blocking platelet TLR2 and TLR4 with mAbs reduced the percentage of activated platelets and lowered the amount of thrombin generated in PRP. These data show that histone-activated platelets possess a procoagulant phenotype that drives plasma thrombin generation and suggest that TLR2 and TLR4 mediate the activation process.
Figures
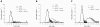
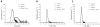
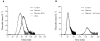
Comment in
-
Inflammation & the platelet histone trap.Blood. 2011 Aug 18;118(7):1714-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-362764. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21852442 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jahr S, Hentze H, Englisch S, et al. DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61(4):1659–1665. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, Laube B, Abu Abed U, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303(5663):1532–1535. - PubMed
-
- von Köckritz-Blickwede M, Goldmann O, Thulin P, et al. Phagocytosis-independent antimicrobial activity of mast cells by means of extracellular trap formation. Blood. 2008;111(6):3070–3080. - PubMed
-
- Holdenrieder S, Stieber P. Clinical use of circulating nucleosomes. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2009;46(1):1–24. - PubMed
-
- Zeerleder S, Zwart B, Wuillemin WA, et al. Elevated nucleosome levels in systemic inflammation and sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2003;31(7):1947–1951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

