Changes in global gene expression in response to chemical and genetic perturbation of chromatin structure
- PMID: 21673996
- PMCID: PMC3108824
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020587
Changes in global gene expression in response to chemical and genetic perturbation of chromatin structure
Abstract
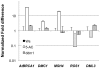
DNA methylation is important for controlling gene expression in all eukaryotes. Microarray analysis of mutant and chemically-treated Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings with reduced DNA methylation revealed an altered gene expression profile after treatment with the DNA methylation inhibitor 5-aza-2' deoxycytidine (5-AC), which included the upregulation of expression of many transposable elements. DNA damage-response genes were also coordinately upregulated by 5-AC treatment. In the ddm1 mutant, more specific changes in gene expression were observed, in particular for genes predicted to encode transposable elements in centromeric and pericentromeric locations. These results confirm that DDM1 has a very specific role in maintaining transcriptional silence of transposable elements, while chemical inhibitors of DNA methylation can affect gene expression at a global level.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Jackson JP, Lindroth AM, Cao X, Jacobsen SE. Control of CpNpG DNA methylation by the KRYPTONITE histone H3 methyltransferase. Nature. 2002;416:556–560. - PubMed
-
- Cao X, Aufsatz W, Zilberman D, Mette MF, Huang MS, et al. Role of the DRM and CMT3 methyltransferases in RNA-directed DNA methylation. Curr Biol. 2003;13:2212–2217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

