An interactive voice response diary for patients with non-dystrophic myotonia
- PMID: 21674518
- PMCID: PMC3233757
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.22007
An interactive voice response diary for patients with non-dystrophic myotonia
Abstract
Introduction: Non-dystrophic myotonia (NDM) is caused by mutations in muscle chloride and sodium channels. Currently, there is no standardized instrument for documenting symptom frequency and severity in NDM.
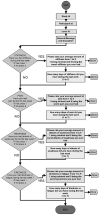
Methods: Subjects used an automated, interactive, telephone-based voice response diary (IVR) to record frequency and severity of stiffness, weakness, pain, and tiredness once a week for 8 weeks, after their baseline visits.
Results: We describe the IVR and report data on 76 subjects for a total of 385 person-weeks. Overall there were 5.1 calls per subject. Forty-eight subjects called in 5 or more times, and 14 called in 8 times. Stiffness was both the most frequent and severe symptom. Warm-up and handgrip myotonia were associated with higher severity scores for stiffness.
Conclusions: IVR is a convenient technology to allow patient reporting of repeated and real-time symptom frequency and severity, and it is presently being used in a trial of mexiletine in NDM.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Cannon SC. Spectrum of sodium channel disturbances in the nondystrophic myotonias and periodic paralyses. Kidney Int. 2000;57(3):772–9. - PubMed
-
- Colding-Jorgensen E. Phenotypic variability in myotonia congenita. Muscle Nerve. 2005;32(1):19–34. - PubMed
-
- Ptacek L. The familial periodic paralyses and nondystrophic myotonias. Am J Med. 1998;105(1):58–70. - PubMed
-
- Ptacek LJ, Johnson KJ, Griggs RC. Genetics and physiology of the myotonic muscle disorders. N Engl J Med. 1993;328(7):482–9. - PubMed
-
- Fialho D, et al. Chloride channel myotonia: exon 8 hot-spot for dominant-negative interactions. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 12):3265–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

