Motor imagery evokes increased somatosensory activity in Parkinson's disease patients with tremor
- PMID: 21674693
- PMCID: PMC6869863
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21318
Motor imagery evokes increased somatosensory activity in Parkinson's disease patients with tremor
Abstract
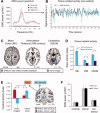
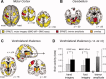
Parkinson's disease (PD) is surprisingly heterogeneous: some patients have a prominent resting tremor, while others never develop this symptom. Here we investigate whether the functional organization of the voluntary motor system differs between PD patients with and without resting tremor, and whether these differences relate to the cerebral circuit producing tremor. We compared 18 PD patients with marked tremor, 20 PD patients without tremor, and 19 healthy controls. Subjects performed a controlled motor imagery task during fMRI scanning. We quantified imagery-related cerebral activity by contrasting imagery of biomechanically difficult and easy movements. Tremor-related activity was identified by relating cerebral activity to fluctuations in tremor amplitude, using electromyography during scanning. PD patients with tremor had better behavioral performance than PD patients without tremor. Furthermore, tremulous PD patients showed increased imagery-related activity in somatosensory area 3a, as compared with both healthy controls and to nontremor PD patients. This effect was independent from tremor-related activity, which was localized to the motor cortex, cerebellum, and thalamic ventral intermediate nucleus (VIM). The VIM, with known projections to area 3a, was unique in showing both tremor- and imagery-related responses. We conclude that parkinsonian tremor influences motor imagery by modulating central somatosensory processing through the VIM. This mechanism may explain clinical differences between PD patients with and without tremor.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Alves G, Larsen JP, Emre M, Wentzel‐Larsen T, Aarsland D ( 2006): Changes in motor subtype and risk for incident dementia in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 21: 1123–1130. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston K ( 1997): Multimodal image coregistration and partitioning—A unified framework. Neuroimage 6: 209–217. - PubMed
-
- Behrens TE, Johansen‐Berg H, Woolrich MW, Smith SM, Wheeler‐Kingshott CA, Boulby PA, Barker GJ, Sillery EL, Sheehan K, Ciccarelli O, Thompson AJ, Brady JM, Matthews PM ( 2003): Non‐invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nat Neurosci 6: 750–757. - PubMed
-
- Benabid AL, Pollak P, Gervason C, Hoffmann D, Gao DM, Hommel M, Perret JE, de Rougemont J ( 1991): Long‐term suppression of tremor by chronic stimulation of the ventral intermediate thalamic nucleus. Lancet 337: 403–406. - PubMed
-
- Beuter A, Barbo E, Rigal R, Blanchet PJ ( 2005): Characterization of subclinical tremor in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 20: 945–950. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

