Diagnostic shifts during the decade following first admission for psychosis
- PMID: 21676994
- PMCID: PMC3589618
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11010048
Diagnostic shifts during the decade following first admission for psychosis
Abstract
Objective: Diagnostic shifts have been prospectively examined in the short term, but the long-term stability of diagnoses has rarely been evaluated. The authors examined diagnostic shifts over a 10-year follow-up period.
Method: A cohort of 470 first-admission patients with psychotic disorders was systematically assessed at baseline and at 6-month, 2-year, and 10-year follow-ups. Longitudinal best-estimate consensus diagnoses were formulated after each assessment.
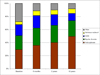
Results: At baseline, the diagnostic distribution was 29.6% schizophrenia spectrum disorders, 21.1% bipolar disorder with psychotic features, 17.0% major depression with psychotic features, 2.4% substance-induced psychosis, and 27.9% other psychoses. At year 10, the distribution changed to 49.8%, 24.0%, 11.1%, 7.0%, and 8.1%, respectively. Overall, diagnoses were changed for 50.7% of study participants at some point during the study. Most participants who were initially diagnosed with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder retained the diagnosis at year 10 (89.2% and 77.8%, respectively). However, 32.0% of participants (N=98) originally given a non-schizophrenia diagnosis had gradually shifted to a schizophrenia diagnosis by year 10. The second largest shift was to bipolar disorder (10.7% of those not given this diagnosis at baseline). Changes in the clinical picture explained many diagnostic shifts. In particular, poorer functioning and greater negative and psychotic symptom ratings predicted a subsequent shift to schizophrenia. Better functioning and lower negative and depressive symptom ratings predicted the shift to bipolar disorder.
Conclusions: First-admission patients with psychotic disorders run the risk of being misclassified at early stages in the illness course, including more than 2 years after first hospitalization. Diagnosis should be reassessed at all follow-up points.
Figures
Comment in
-
Diagnostic instability: how much is too much?Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Nov;168(11):1136-8. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11081191. Am J Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 22193597 No abstract available.
References
-
- Robins E, Guze SB. Establishment of diagnostic validity in psychiatric illness: its application to schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1970;126:983–987. - PubMed
-
- Kendler KS. The impact of diagnostic misclassification on the pattern of familial aggregation and coaggregation of psychiatric illness. J Psychiatr Res. 1987;21:55–91. - PubMed
-
- Chang WC, Chan SSM, Chung DWS. Diagnostic stability of functional psychosis: a systematic review. Hong Kong J Psychiatry. 2009;19:30–41.
-
- Craig TJ, Fennig S, Tanenberg-Karant M, Bromet EJ. Rapid vs delayed readmission in first-admission psychosis: quality indicators for managed care? Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2000;12:233–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

