Essential roles of enteric neuronal serotonin in gastrointestinal motility and the development/survival of enteric dopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 21677183
- PMCID: PMC4442094
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6684-10.2011
Essential roles of enteric neuronal serotonin in gastrointestinal motility and the development/survival of enteric dopaminergic neurons
Abstract
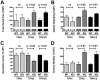
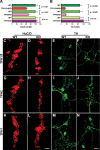
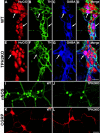
The gut contains a large 5-HT pool in enterochromaffin (EC) cells and a smaller 5-HT pool in the enteric nervous system (ENS). During development, enteric neurons are generated asynchronously. We tested hypotheses that serotonergic neurons, which arise early, affect development/survival of later-born dopaminergic, GABAergic, nitrergic, and calcitonin gene-related peptide-expressing neurons and are essential for gastrointestinal motility. 5-HT biosynthesis depends on tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH1) in EC cells and on TPH2 in neurons; therefore, mice lacking TPH1 and/or TPH2 distinguish EC-derived from neuronal 5-HT. Deletion of TPH2, but not TPH1, decreased myenteric neuronal density and proportions of dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons but did not affect the extrinsic sympathetic innervation of the gut; intestinal transit slowed in mice lacking TPH2 mice, but gastric emptying accelerated. Isolated enteric crest-derived cells (ENCDCs) expressed the serotonin reuptake transporter (SERT) and 15 subtypes of 5-HT receptor. Addition of 5-HT to cultures of isolated ENCDCs promoted total and dopaminergic neuronal development. Rings of SERT-immunoreactive terminal axons surrounded myenteric dopaminergic neurons and SERT knock-out increased intestinal levels of dopamine metabolites, implying that enteric dopaminergic neurons receive a serotonergic innervation. Observations suggest that constitutive gastrointestinal motility depends more on neuronal than EC cell serotonin; moreover, serotonergic neurons promote development/survival of some classes of late-born enteric neurons, including dopaminergic neurons, which appear to innervate and activate in the adult ENS.
Figures





References
-
- Bertrand PP. Real-time detection of serotonin release from enterochromaffin cells of the guinea-pig ileum. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004;16:511–514. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand PP, Bertrand RL. Serotonin release and uptake in the gastrointestinal tract. Auton Neurosci. 2010;153:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand PP, Hu X, Mach J, Bertrand RL. Serotonin (5-HT) release and uptake measured by real-time electrochemical techniques in the rat ileum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;295:G1228–G1236. - PubMed
-
- Blaugrund E, Pham TD, Tennyson VM, Lo L, Sommer L, Anderson DJ, Gershon MD. Distinct subpopulations of enteric neuronal progenitors defined by time of development, sympathoadrenal lineage markers, and Mash-1-dependence. Development. 1996;122:309–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
