A haploid genetic screen identifies the major facilitator domain containing 2A (MFSD2A) transporter as a key mediator in the response to tunicamycin
- PMID: 21677192
- PMCID: PMC3141996
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1018098108
A haploid genetic screen identifies the major facilitator domain containing 2A (MFSD2A) transporter as a key mediator in the response to tunicamycin
Abstract
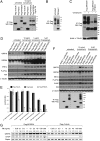
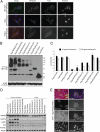
Tunicamycin (TM) inhibits eukaryotic asparagine-linked glycosylation, protein palmitoylation, ganglioside production, proteoglycan synthesis, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A reductase activity, and cell wall biosynthesis in bacteria. Treatment of cells with TM elicits endoplasmic reticulum stress and activates the unfolded protein response. Although widely used in laboratory settings for many years, it is unknown how TM enters cells. Here, we identify in an unbiased genetic screen a transporter of the major facilitator superfamily, major facilitator domain containing 2A (MFSD2A), as a critical mediator of TM toxicity. Cells without MFSD2A are TM-resistant, whereas MFSD2A-overexpressing cells are hypersensitive. Hypersensitivity is associated with increased cellular TM uptake concomitant with an enhanced endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Furthermore, MFSD2A mutant analysis reveals an important function of the C terminus for correct intracellular localization and protein stability, and it identifies transmembrane helical amino acid residues essential for mediating TM sensitivity. Overall, our data uncover a critical role for MFSD2A by acting as a putative TM transporter at the plasma membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Knocking out the door to tunicamycin entry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 19;108(29):11731-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109035108. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21734150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tsvetanova BC, Kiemle DJ, Price NP. Biosynthesis of tunicamycin and metabolic origin of the 11-carbon dialdose sugar, tunicamine. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35289–35296. - PubMed
-
- Takatsuki A, Tamura G. Effect of tunicamycin on the synthesis of macromolecules in cultures of chick embryo fibroblasts infected with Newcastle disease virus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971;24:785–794. - PubMed
-
- Heifetz A, Keenan RW, Elbein AD. Mechanism of action of tunicamycin on the UDP-GlcNAc:dolichyl-phosphate Glc-NAc-1-phosphate transferase. Biochemistry. 1979;18:2186–2192. - PubMed
-
- Keller RK, Boon DY, Crum FC. N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase from hen oviduct: Solubilization, characterization, and inhibition by tunicamycin. Biochemistry. 1979;18:3946–3952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

