Suppression of HTLV-1 replication by Tax-mediated rerouting of the p13 viral protein to nuclear speckles
- PMID: 21677314
- PMCID: PMC3156045
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-293340
Suppression of HTLV-1 replication by Tax-mediated rerouting of the p13 viral protein to nuclear speckles
Abstract
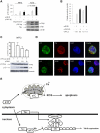
Disease development in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1)-infected individuals is positively correlated with the level of integrated viral DNA in T cells. HTLV-1 replication is positively regulated by Tax and Rex and negatively regulated by the p30 and HBZ proteins. In the present study, we demonstrate that HTLV-1 encodes another negative regulator of virus expression, the p13 protein. Expressed separately, p13 localizes to the mitochondria, whereas in the presence of Tax, part of it is ubiquitinated, stabilized, and rerouted to the nuclear speckles. The p13 protein directly binds Tax, decreases Tax binding to the CBP/p300 transcriptional coactivator, and, by reducing Tax transcriptional activity, suppresses viral expression. Because Tax stabilizes its own repressor, these findings suggest that HTLV-1 has evolved a complex mechanism to control its own replication. Further, these results highlight the importance of studying the function of the HTLV-1 viral proteins, not only in isolation, but also in the context of full viral replication.
Figures
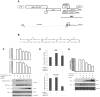
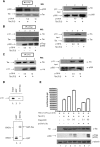
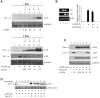
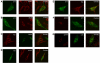
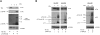
References
-
- Gessain A. Virological aspects of tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I associated myelopathy and HTLV-I infection. J Neurovirol. 1996;2(5):299–306. - PubMed
-
- Osame M. Pathological mechanisms of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). J Neurovirol. 2002;8(5):359–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

