NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses
- PMID: 21677641
- PMCID: PMC3172695
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10130
NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses
Abstract
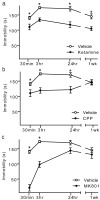
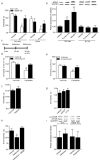
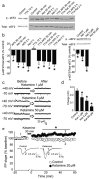
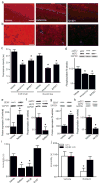
Clinical studies consistently demonstrate that a single sub-psychomimetic dose of ketamine, an ionotropic glutamatergic NMDAR (N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor) antagonist, produces fast-acting antidepressant responses in patients suffering from major depressive disorder, although the underlying mechanism is unclear. Depressed patients report the alleviation of major depressive disorder symptoms within two hours of a single, low-dose intravenous infusion of ketamine, with effects lasting up to two weeks, unlike traditional antidepressants (serotonin re-uptake inhibitors), which take weeks to reach efficacy. This delay is a major drawback to current therapies for major depressive disorder and faster-acting antidepressants are needed, particularly for suicide-risk patients. The ability of ketamine to produce rapidly acting, long-lasting antidepressant responses in depressed patients provides a unique opportunity to investigate underlying cellular mechanisms. Here we show that ketamine and other NMDAR antagonists produce fast-acting behavioural antidepressant-like effects in mouse models, and that these effects depend on the rapid synthesis of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. We find that the ketamine-mediated blockade of NMDAR at rest deactivates eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) kinase (also called CaMKIII), resulting in reduced eEF2 phosphorylation and de-suppression of translation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Furthermore, we find that inhibitors of eEF2 kinase induce fast-acting behavioural antidepressant-like effects. Our findings indicate that the regulation of protein synthesis by spontaneous neurotransmission may serve as a viable therapeutic target for the development of fast-acting antidepressants.
©2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
Figures
Comment in
-
Mood disorders: targeting protein synthesis for fast antidepressant action.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Aug 1;10(8):577. doi: 10.1038/nrd3520. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21804593 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zarate CA, Jr, et al. A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(8):856–864. - PubMed
-
- Berman RM, et al. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;47(4):351–354. - PubMed
-
- Maeng S, et al. Cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of ketamine: role of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63(4):349–352. - PubMed
-
- Detke MJ, Johnson J, Lucki I. Acute and chronic antidepressant drug treatment in the rat forced swimming test model of depression. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 1997;5(2):107–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

