Combined Striatum, Brain Stem, and Optic Nerve Involvement due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in an Ambulatory Child
- PMID: 21677880
- PMCID: PMC3104858
- DOI: 10.1159/000328836
Combined Striatum, Brain Stem, and Optic Nerve Involvement due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in an Ambulatory Child
Abstract
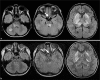
In children, Mycoplasma pneumoniae encephalitis has been characterized by acute onset of an encephalopathy associated with extrapyramidal symptoms and symmetric basal ganglia with or without brain stem involvement on magnetic resonance imaging. Our case, showing unilateral optic neuritis, ophthalmoplegia, no extrapyramidal symptoms, and typical striatal involvement on magnetic resonance imaging, broadens the spectrum of varying clinical manifestations of childhood M. pneumoniae-associated encephalopathy.
Keywords: Basal ganglia; Mycoplasma pneumonia; Optic neuritis.
Figures
References
-
- Bitnun A, Ford-Jones EL, Petric M, MacGregor D, Heurter H, Nelson S, Johnson G, Richardson S. Acute childhood encephalitis and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1674–1684. - PubMed
-
- Saitoh S, Wada T, Narita M, Narita M, Kohsaka S, Mizukami S, Togashi T, Kajii N. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection may cause striatal lesions leading to acute neurologic dysfunction. Neurology. 1993;43:2150–2151. - PubMed
-
- Sakoulas G. Brainstem and striatal encephalitis complicating Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: possible benefit of intravenous immunoglobulin. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:543–545. - PubMed
-
- Narita M. Pathogenesis of neurologic manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Pediatr Neurol. 2009;41:159–166. - PubMed
-
- Schwab S, Jünger E, Spranger M, Dörfler A, Albert F, Steiner HH, Hacke W. Craniectomy: An aggressive treatment approach in severe encephalitis. Neurology. 1997;48:412–417. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

