Short read Illumina data for the de novo assembly of a non-model snail species transcriptome (Radix balthica, Basommatophora, Pulmonata), and a comparison of assembler performance
- PMID: 21679424
- PMCID: PMC3128070
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-317
Short read Illumina data for the de novo assembly of a non-model snail species transcriptome (Radix balthica, Basommatophora, Pulmonata), and a comparison of assembler performance
Abstract
Background: Until recently, read lengths on the Solexa/Illumina system were too short to reliably assemble transcriptomes without a reference sequence, especially for non-model organisms. However, with read lengths up to 100 nucleotides available in the current version, an assembly without reference genome should be possible. For this study we created an EST data set for the common pond snail Radix balthica by Illumina sequencing of a normalized transcriptome. Performance of three different short read assemblers was compared with respect to: the number of contigs, their length, depth of coverage, their quality in various BLAST searches and the alignment to mitochondrial genes.
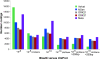
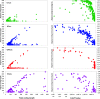
Results: A single sequencing run of a normalized RNA pool resulted in 16,923,850 paired end reads with median read length of 61 bases. The assemblies generated by VELVET, OASES, and SeqMan NGEN differed in the total number of contigs, contig length, the number and quality of gene hits obtained by BLAST searches against various databases, and contig performance in the mt genome comparison. While VELVET produced the highest overall number of contigs, a large fraction of these were of small size (< 200bp), and gave redundant hits in BLAST searches and the mt genome alignment. The best overall contig performance resulted from the NGEN assembly. It produced the second largest number of contigs, which on average were comparable to the OASES contigs but gave the highest number of gene hits in two out of four BLAST searches against different reference databases. A subsequent meta-assembly of the four contig sets resulted in larger contigs, less redundancy and a higher number of BLAST hits.
Conclusion: Our results document the first de novo transcriptome assembly of a non-model species using Illumina sequencing data. We show that de novo transcriptome assembly using this approach yields results useful for downstream applications, in particular if a meta-assembly of contig sets is used to increase contig quality. These results highlight the ongoing need for improvements in assembly methodology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comparing de novo assemblers for 454 transcriptome data.BMC Genomics. 2010 Oct 16;11:571. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-571. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20950480 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly and annotation of a non-model gastropod (Nerita melanotragus) transcriptome: a comparison of de novo assemblers.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Aug 1;7:488. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-488. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25084827 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative performance of transcriptome assembly methods for non-model organisms.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jul 27;17:523. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2923-8. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27464550 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for transcriptome analysis in nonmodel plants.Am J Bot. 2012 Feb;99(2):267-76. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1100334. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Am J Bot. 2012. PMID: 22301897 Review.
-
De novo assembly of transcriptomes and differential gene expression analysis using short-read data from emerging model organisms - a brief guide.Front Zool. 2024 Jun 20;21(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12983-024-00538-y. Front Zool. 2024. PMID: 38902827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathways associated with lignin biosynthesis in lignomaniac jute fibres.Mol Genet Genomics. 2015 Aug;290(4):1523-42. doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-1013-y. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25724692
-
Optimized deep-targeted proteotranscriptomic profiling reveals unexplored Conus toxin diversity and novel cysteine frameworks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 21;112(29):E3782-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501334112. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26150494 Free PMC article.
-
The venom-gland transcriptome of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus).BMC Genomics. 2012 Jul 16;13:312. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-312. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23025625 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomics Analysis of Crassostrea hongkongensis for the Discovery of Reproduction-Related Genes.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 10;10(8):e0134280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134280. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26258576 Free PMC article.
-
De novo sequence assembly and characterisation of a partial transcriptome for an evolutionarily distinct reptile, the tuatara (Sphenodon punctatus).BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 31;13:439. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-439. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22938396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouck A, Vision T. The molecular ecologist's guide to expressed sequence tags. Mol Ecol. 2007;16(5):907–924. - PubMed
-
- Bacchetti De Gregoris T, Borra M, Biffali E, Bekel T, Burgess J, Kirby R, Clare A. Construction of an adult barnacle (Balanus amphitrite) cDNA library and selection of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR studies. BMC Molecular Biology. 2009;10(1):62. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-62. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

