Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 is a cellular factor required for hepatitis C virus propagation
- PMID: 21680504
- PMCID: PMC3165832
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02533-10
Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 is a cellular factor required for hepatitis C virus propagation
Abstract
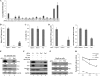
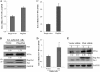
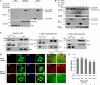
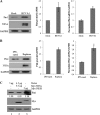
The life cycle of hepatitis C virus (HCV) is highly dependent on cellular factors. Using small interfering RNA (siRNA) library screening, we identified peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 (Pin1) as a host factor involved in HCV propagation. Here we demonstrated that silencing of Pin1 expression resulted in decreases in HCV replication in both HCV replicon cells and cell culture-grown HCV (HCVcc)-infected cells, whereas overexpression of Pin1 increased HCV replication. Pin1 interacted with both the NS5A and NS5B proteins. However, Pin1 expression was increased only by the NS5B protein. Both the protein binding and isomerase activities of Pin1 were required for HCV replication. Juglone, a natural inhibitor of Pin1, inhibited HCV propagation by inhibiting the interplay between the Pin1 and HCV NS5A/NS5B proteins. These data indicate that Pin1 modulates HCV propagation and may contribute to HCV-induced liver pathogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nonstructural 5A Protein of Hepatitis C Virus Regulates Soluble Resistance-Related Calcium-Binding Protein Activity for Viral Propagation.J Virol. 2015 Dec 30;90(6):2794-805. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02493-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26719254 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 associates with insulin receptor substrate-1 and enhances insulin actions and adipogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 10;286(23):20812-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.206904. Epub 2011 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454638 Free PMC article.
-
Pin1 interacts with the Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase catalytic subunit and regulates viral DNA replication.J Virol. 2013 Feb;87(4):2120-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02634-12. Epub 2012 Dec 5. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23221557 Free PMC article.
-
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003;5:477-87. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003. PMID: 14593743 Review.
-
[Pin1: a multi-talented peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase and a promising therapeutic target for human cancers].Med Sci (Paris). 2014 Aug-Sep;30(8-9):772-8. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20143008015. Epub 2014 Sep 1. Med Sci (Paris). 2014. PMID: 25174754 Review. French.
Cited by
-
ADP-ribosylation Factor-related Protein 1 Interacts with NS5A and Regulates Hepatitis C Virus Propagation.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 23;6:31211. doi: 10.1038/srep31211. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27550144 Free PMC article.
-
The kingdom of the prolyl-isomerase Pin1: The structural and functional convergence and divergence of Pin1.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 30;10:956071. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.956071. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36111342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2, periodontal pathogens, and host factors: The trinity of oral post-acute sequelae of COVID-19.Rev Med Virol. 2024 May;34(3):e2543. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2543. Rev Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 38782605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Nonstructural 5A Protein Interacts with Abelson Interactor 1 and Modulates Epidermal Growth Factor-mediated MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 21;291(43):22607-22617. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.727081. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27551040 Free PMC article.
-
Saponin inhibits hepatitis C virus propagation by up-regulating suppressor of cytokine signaling 2.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039366. Epub 2012 Jun 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22745742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choi S. H., Hwang S. B. 2006. Modulation of the transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction pathway by hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein. J. Biol. Chem. 281:7468–7478 - PubMed
-
- Choi S. H., Jeong S. H., Hwang S. B. 2007. Large hepatitis delta antigen modulates transforming growth factor-beta signaling cascades: implication of hepatitis delta virus-induced liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 132:343–357 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

