The yeast p24 complex regulates GPI-anchored protein transport and quality control by monitoring anchor remodeling
- PMID: 21680708
- PMCID: PMC3154887
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0294
The yeast p24 complex regulates GPI-anchored protein transport and quality control by monitoring anchor remodeling
Abstract
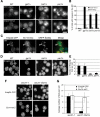
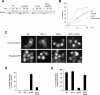
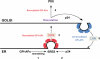
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins are secretory proteins that are attached to the cell surface of eukaryotic cells by a glycolipid moiety. Once GPI anchoring has occurred in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the structure of the lipid part on the GPI anchor undergoes a remodeling process prior to ER exit. In this study, we provide evidence suggesting that the yeast p24 complex, through binding specifically to GPI-anchored proteins in an anchor-dependent manner, plays a dual role in their selective trafficking. First, the p24 complex promotes efficient ER exit of remodeled GPI-anchored proteins after concentration by connecting them with the COPII coat and thus facilitates their incorporation into vesicles. Second, it retrieves escaped, unremodeled GPI-anchored proteins from the Golgi to the ER in COPI vesicles. Therefore the p24 complex, by sensing the status of the GPI anchor, regulates GPI-anchored protein intracellular transport and coordinates this with correct anchor remodeling.
Figures

References
-
- Belden WJ, Barlowe C. Erv25p, a component of COPII-coated vesicles, forms a complex with Emp24p that is required for efficient endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:26939–26946. - PubMed
-
- Belden WJ, Barlowe C. Distinct roles for the cytoplasmic tail sequences of Emp24p and Erv25p in transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:43040–43048. - PubMed
-
- Bonnon C, Wendeler MW, Paccaud JP, Hauri HP. Selective export of human GPI-anchored proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:1705–1715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

