SIRT6 promotes DNA repair under stress by activating PARP1
- PMID: 21680843
- PMCID: PMC5472447
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1202723
SIRT6 promotes DNA repair under stress by activating PARP1
Abstract
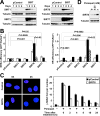
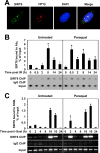
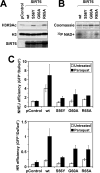
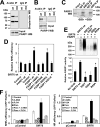
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) is a mammalian homolog of the yeast Sir2 deacetylase. Mice deficient for SIRT6 exhibit genome instability. Here, we show that in mammalian cells subjected to oxidative stress SIRT6 is recruited to the sites of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and stimulates DSB repair, through both nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination. Our results indicate that SIRT6 physically associates with poly[adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1) and mono-ADP-ribosylates PARP1 on lysine residue 521, thereby stimulating PARP1 poly-ADP-ribosylase activity and enhancing DSB repair under oxidative stress.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

