Methyl jasmonate signaling and signal crosstalk between methyl jasmonate and abscisic acid in guard cells
- PMID: 21681023
- PMCID: PMC3257766
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.6.7.15439
Methyl jasmonate signaling and signal crosstalk between methyl jasmonate and abscisic acid in guard cells
Abstract
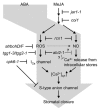
Plants tightly control stomatal aperture in response to various environmental changes. A drought-inducible phytohormone, abscisic acid (ABA), triggers stomatal closure and ABA signaling pathway in guard cells has been well studied. Similar to ABA, methyl jasmonate (MeJA) induces stomatal closure in various plant species but MeJA signaling pathway is still far from clear. Recently we found that Arabidopsis calcium dependent protein kinase CPK6 functions as a positive regulator in guard cell MeJA signaling and provided new insights into cytosolic Ca2+-dependent MeJA signaling. Here we discuss the MeJA signaling and also signal crosstalk between MeJA and ABA pathways in guard cells.
Figures
References
-
- Shimazaki K, Doi M, Assmann SM, Kinoshita T. Light regulation of stomatal movement. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2007;58:219–247. - PubMed
-
- Tsonev TD, Lazova GN, Stoinova ZG, Popova LP. A possible role for jasmonic acid in adaptation of barley seedlings to salinity stress. J Plant Growth Regul. 1998;17:153–159.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
