Efficacy of HLA-DRB1∗03:01 and H2E transgenic mouse strains to correlate pathogenic thyroglobulin epitopes for autoimmune thyroiditis
- PMID: 21683551
- PMCID: PMC3173590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.05.010
Efficacy of HLA-DRB1∗03:01 and H2E transgenic mouse strains to correlate pathogenic thyroglobulin epitopes for autoimmune thyroiditis
Abstract
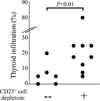
Thyroglobulin (Tg), a homodimer of 660 kD comprising 2748 amino acids, is the largest autoantigen known. The prevalence of autoimmune thyroid disease, including Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease, has provided the impetus for identifying pathogenic T cell epitopes from human Tg over two decades. With no known dominant epitopes, the search has long been a challenge for investigators. After identifying HLA-DRB1∗03:01 (HLA-DR3) and H2E(b) as susceptibility alleles for Tg-induced experimental autoimmune thyroiditis in transgenic mouse strains, we searched for naturally processed T cell epitopes with MHC class II-binding motif anchors and tested the selected peptides for pathogenicity in these mice. The thyroiditogenicity of one peptide, hTg2079, was confirmed in DR3 transgenic mice and corroborated in clinical studies. In H2E(b)-expressing transgenic mice, we identified three T cell epitopes from mouse Tg, mTg179, mTg409 and mTg2342, based on homology to epitopes hTg179, hTg410 and hTg2344, respectively, which we and others have found stimulatory or pathogenic in both DR3- and H2E-expressing mice. The high homology among these peptides with shared presentation by DR3, H2E(b) and H2E(k) molecules led us to examine the binding pocket residues of these class II molecules. Their similar binding characteristics help explain the pathogenic capacity of these T cell epitopes. Our approach of using appropriate human and murine MHC class II transgenic mice, combined with the synthesis and testing of potential pathogenic Tg peptides predicted from computational models of MHC-binding motifs, should continue to provide insights into human autoimmune thyroid disease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Vladutiu AO, Rose NR. Autoimmune murine thyroiditis: relation to histocompatibility (H-2) type. Science. 1971;174:1137–1139. - PubMed
-
- ElRehewy M, Kong YM, Giraldo AA, Rose NR. Syngeneic thyroglobulin is immunogenic in good responder mice. Eur J Immunol. 1981;11:146–151. - PubMed
-
- Beisel KW, David CS, Giraldo AA, Kong YM, Rose NR. Regulation of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis: mapping of susceptibility to the I-A subregion of the mouse H-2. Immunogenetics. 1982;15:427–431. - PubMed
-
- Kong YM, David CS, Giraldo AA, ElRehewy M, Rose NR. Regulation of autoimmune response to mouse thyroglobulin: influence of H-2D-end genes. J Immunol. 1979;123:15–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

