Shortening the xerostomia inventory
- PMID: 21684773
- PMCID: PMC3154566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.03.024
Shortening the xerostomia inventory
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to determine the validity and properties of the Summated Xerostomia Inventory-Dutch Version in samples from Australia, The Netherlands, Japan, and New Zealand.
Study design: Six cross-sectional samples of older people from The Netherlands (n = 50), Australia (n = 637; n = 245), Japan (n = 401), and New Zealand (n = 167; n = 86) were enrolled. Data were analyzed by using the Summated Xerostomia Inventory-Dutch Version.
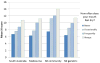
Results: All datasets revealed a single extracted factor which explained about one-half of the variance, with Cronbach alpha values ≥0.70. When mean scale scores were plotted against a "gold-standard" xerostomia question, statistically significant gradients were observed, with the highest score seen in those who always had dry mouth, and the lowest in those who never had it.
Conclusions: The Summated Xerostomia Inventory-Dutch Version is valid for measuring xerostomia symptoms in clinical and epidemiologic research.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ikebe K, Morii K, Kashiwagi J, Nokubi T, Ettinger RL. Impact of dry mouth on oral symptoms and function in removable denture wearers in Japan. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;99:704–10. - PubMed
-
- Locker D. Dental status, xerostomia and the oral health-related quality of life of an elderly institutionalized population. Spec Care Dentist. 2003;23:86–93. - PubMed
-
- Thomson WM. Issues in the epidemiological investigation of dry mouth. Gerodontol. 2005;22:65–76. - PubMed
-
- Thomson WM, Chalmers JM, Spencer AJ, Williams SM. The Xerostomia Inventory: a multi-item approach to measuring dry mouth. Community Dent Health. 1999;16:12–7. - PubMed