Genome-wide association study of smoking behaviours in patients with COPD
- PMID: 21685187
- PMCID: PMC3302576
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200154
Genome-wide association study of smoking behaviours in patients with COPD
Abstract
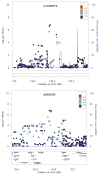
Background Cigarette smoking is a major risk factor for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and COPD severity. Previous genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified numerous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with the number of cigarettes smoked per day (CPD) and a dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH) locus associated with smoking cessation in multiple populations. Objective To identify SNPs associated with lifetime average and current CPD, age at smoking initiation, and smoking cessation in patients with COPD. Methods GWAS were conducted in four independent cohorts encompassing 3441 ever-smoking patients with COPD (Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease stage II or higher). Untyped SNPs were imputed using the HapMap (phase II) panel. Results from all cohorts were meta-analysed. Results Several SNPs near the HLA region on chromosome 6p21 and in an intergenic region on chromosome 2q21 showed associations with age at smoking initiation, both with the lowest p=2×10(-7). No SNPs were associated with lifetime average CPD, current CPD or smoking cessation with p<10(-6). Nominally significant associations with candidate SNPs within cholinergic receptors, nicotinic, alpha 3/5 (CHRNA3/CHRNA5; eg, p=0.00011 for SNP rs1051730) and cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily A, polypeptide 6 (CYP2A6; eg, p=2.78×10(-5) for a non-synonymous SNP rs1801272) regions were observed for lifetime average CPD, however only CYP2A6 showed evidence of significant association with current CPD. A candidate SNP (rs3025343) in DBH was significantly (p=0.015) associated with smoking cessation. Conclusion The authors identified two candidate regions associated with age at smoking initiation in patients with COPD. Associations of CHRNA3/CHRNA5 and CYP2A6 loci with CPD and DBH with smoking cessation are also likely of importance in the smoking behaviours of patients with COPD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00292552.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests: MS, AG
GlaxoSmithKline employee: WA, XK
NHLBI grant: JEH, THB
NIH grant: MHC, EKS, JDC
GlaxoSmithKline grant: EKS, DAL, PB
COPD Foundation grant: EKS, JDC
GlaxoSmithKline consulting fee or honorarium and support for travel to meetings for the study or other purposes: EKS, DAL
COPD Foundation support for travel to meetings for the study or other purposes: EKS, JDC
AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline - payment for lectures including service on speakers bureaus and consultancy (outside the submitted work): EKS, PB
Pfizer - payment for lectures including service on speakers bureaus and consultancy (outside the submitted work): PB
GlaxoSmithKline - board membership, consultancy, payment for lectures including service on speakers bureaus and consultancy (outside the submitted work): DAL
Boehringer Ingelheim consultancy (outside the submitted work): DAL
GlaxoSmithKline fees for participation in review activities such as data monitoring boards, statistical analysis, end point committees, and the like: DAL
Consulting fee or honorarium from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Otsuka: SIR
Grant from AstraZeneca, Biomarck, Centocor, Mpex, Nabi, Novartis, Otsuka: SIR
Almirall, Novartis, Nycomed, Pfizer board membership (outside the submitted work): SIR
Almirall, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, California Allergy Society, Creative Educational Concept, France Foundation, GlaxoSmithKline, Information TV, Network for Continuing Education, Novartis, Nycomed, Pfizer - travel/accommodations expenses covered or reimbursed (outside the submitted work): SIR
Able Associates, Adelphi Research, APT Pharma/Britnall, Aradigm, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, CommonHealth, Consult Complete, COPDForum, Data Monitor, Decision Resource, Defined Health, Dey, Dunn Group, Easton Associates, Equinox, Gerson, GlaxoSmithKline, Infomed, KOL Connection, M. Pankove, MedaCorp, MDRx Financial, Mpex, Oriel Therapeutics, Otsuka, Pennside, PharmaVentures, Pharmaxis, Price Waterhouse, Propagate, Pulmatrix, Reckner Associates, Recruiting Resources, Roche, Schlesinger Medical, Scimed, Sudler and Hennessey, TargeGen, Theravance, UBC, Uptake Medical, VantagePoint Mangement - consultancy (outside the submitted work): SIR
Figures

References
-
- Vink JM, Posthuma D, Neale MC, et al. Genome-wide linkage scan to identify Loci for age at first cigarette in Dutch sibling pairs. Behav Genet. 2006;36:100–11. - PubMed
-
- Li MD, Cheng R, Ma JZ, et al. A meta-analysis of estimated genetic and environmental effects on smoking behavior in male and female adult twins. Addiction. 2003;98:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Batra V, Patkar AA, Berrettini WH, et al. The genetic determinants of smoking. Chest. 2003;123:1730–9. - PubMed
-
- Schnoll RA, Johnson TA, Lerman C. Genetics and smoking behavior. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2007;9:349–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01 HR076103/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076112/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076109/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12HL089990/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HL089990/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076115/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0901786/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL083069/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G0701127/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HR076114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL097029/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076113/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076110/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076119/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076108/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076106/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
