Notch signaling regulates mouse and human Th17 differentiation
- PMID: 21685328
- PMCID: PMC3131467
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003658
Notch signaling regulates mouse and human Th17 differentiation
Abstract
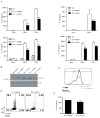
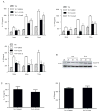
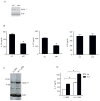
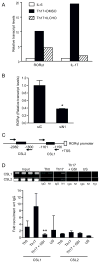
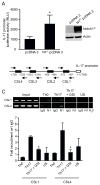
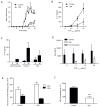
Th17 cells are known to play a critical role in adaptive immune responses to several important extracellular pathogens. Additionally, Th17 cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune and inflammatory disorders as well as in cancer. Therefore, it is essential to understand the mechanisms that regulate Th17 differentiation. Notch signaling is known to be important at several stages of T cell development and differentiation. In this study, we report that Notch1 is activated in both mouse and human in vitro-polarized Th17 cells and that blockade of Notch signaling significantly downregulates the production of Th17-associated cytokines, suggesting an intrinsic requirement for Notch during Th17 differentiation in both species. We also present evidence, using promoter reporter assays, knockdown studies, as well as chromatin immunoprecipitation, that IL-17 and retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γt are direct transcriptional targets of Notch signaling in Th17 cells. Finally, in vivo inhibition of Notch signaling reduced IL-17 production and Th17-mediated disease progression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Thus, this study highlights the importance of Notch signaling in Th17 differentiation and indicates that selective targeted therapy against Notch may be an important tool to treat autoimmune disorders, including multiple sclerosis.
Figures
References
-
- Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:821–852. - PubMed
-
- Cua DJ, Sherlock J, Chen Y, Murphy CA, Joyce B, Seymour B, Lucian L, To W, Kwan S, Churakova T, Zurawski S, Wiekowski M, Lira SA, Gorman D, Kastelein RA, Sedgwick JD. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 2003;421:744–748. - PubMed
-
- Matusevicius D, Kivisakk P, He B, Kostulas N, Ozenci V, Fredrikson S, Link H. Interleukin-17 mRNA expression in blood and CSF mononuclear cells is augmented in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 1999;5:101–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

