Intravenous gammaglobulin suppresses inflammation through a novel T(H)2 pathway
- PMID: 21685887
- PMCID: PMC3694429
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10134
Intravenous gammaglobulin suppresses inflammation through a novel T(H)2 pathway
Abstract
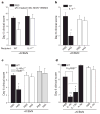
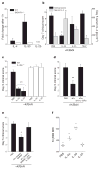
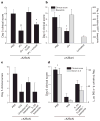
High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin is a widely used therapeutic preparation of highly purified immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies. It is administered at high doses (1-2 grams per kilogram) for the suppression of autoantibody-triggered inflammation in a variety of clinical settings. This anti-inflammatory activity of intravenous immunoglobulin is triggered by a minor population of IgG crystallizable fragments (Fcs), with glycans terminating in α2,6 sialic acids (sFc) that target myeloid regulatory cells expressing the lectin dendritic-cell-specific ICAM-3 grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN; also known as CD209). Here, to characterize this response in detail, we generated humanized DC-SIGN mice (hDC-SIGN), and demonstrate that the anti-inflammatory activity of intravenous immunoglobulin can be recapitulated by the transfer of bone-marrow-derived sFc-treated hDC-SIGN(+) macrophages or dendritic cells into naive recipients. Furthermore, sFc administration results in the production of IL-33, which, in turn, induces expansion of IL-4-producing basophils that promote increased expression of the inhibitory Fc receptor FcγRIIB on effector macrophages. Systemic administration of the T(H)2 cytokines IL-33 or IL-4 upregulates FcγRIIB on macrophages, and suppresses serum-induced arthritis. Consistent with these results, transfer of IL-33-treated basophils suppressed induced arthritic inflammation. This novel DC-SIGN-T(H)2 pathway initiated by an endogenous ligand, sFc, provides an intrinsic mechanism for maintaining immune homeostasis that could be manipulated to provide therapeutic benefit in autoimmune diseases.
©2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
Figures

Comment in
-
Immunotherapy: pieces of the IVIG anti-inflammatory response.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Jul 8;11(8):499. doi: 10.1038/nri3026. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21738217 No abstract available.
-
Literature Watch: implications for transplantation.Am J Transplant. 2012 Oct;12(10):2567. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04297.x. Am J Transplant. 2012. PMID: 23009135 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

