Alpha cells secrete acetylcholine as a non-neuronal paracrine signal priming beta cell function in humans
- PMID: 21685896
- PMCID: PMC3132226
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2371
Alpha cells secrete acetylcholine as a non-neuronal paracrine signal priming beta cell function in humans
Abstract
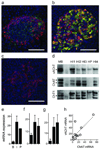
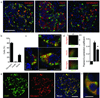
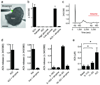
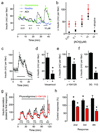
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that has a major role in the function of the insulin-secreting pancreatic beta cell. Parasympathetic innervation of the endocrine pancreas, the islets of Langerhans, has been shown to provide cholinergic input to the beta cell in several species, but the role of autonomic innervation in human beta cell function is at present unclear. Here we show that, in contrast to the case in mouse islets, cholinergic innervation of human islets is sparse. Instead, we find that the alpha cells of human islets provide paracrine cholinergic input to surrounding endocrine cells. Human alpha cells express the vesicular acetylcholine transporter and release acetylcholine when stimulated with kainate or a lowering in glucose concentration. Acetylcholine secretion by alpha cells in turn sensitizes the beta cell response to increases in glucose concentration. Our results demonstrate that in human islets acetylcholine is a paracrine signal that primes the beta cell to respond optimally to subsequent increases in glucose concentration. Cholinergic signaling within islets represents a potential therapeutic target in diabetes, highlighting the relevance of this advance to future drug development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alpha cell regulation of beta cell function.Diabetologia. 2020 Oct;63(10):2064-2075. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05196-3. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 32894317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of insulin secretion by cholinergic signaling in the human pancreatic islet.Diabetes. 2014 Aug;63(8):2714-26. doi: 10.2337/db13-1371. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24658304 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of proglucagon to GLP-1 in pancreatic α-cells: is this a paracrine mechanism enabling GLP-1 to act on β-cells?J Endocrinol. 2011 Oct;211(1):99-106. doi: 10.1530/JOE-11-0094. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21795304
-
[Pax4 transdifferentiates glucagon-secreting alpha cells to insulin-secreting beta endocrine pancreatic cells].Med Sci (Paris). 2009 Aug-Sep;25(8-9):763-5. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2009258-9763. Med Sci (Paris). 2009. PMID: 19765395 French. No abstract available.
-
Beta-cell M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors as potential targets for novel antidiabetic drugs.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Apr;81:106267. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106267. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32044662 Review.
Cited by
-
Design Principles of Pancreatic Islets: Glucose-Dependent Coordination of Hormone Pulses.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 1;11(4):e0152446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152446. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27035570 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinesterases as biomarkers for parasympathetic dysfunction and inflammation-related disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2014 Jul;53(3):298-305. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-0176-4. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24254221 Review.
-
Inter-organ communication and regulation of beta cell function.Diabetologia. 2016 Apr;59(4):659-67. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3862-7. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26791990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paracrine regulation of glucagon secretion: the β/α/δ model.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Apr 15;310(8):E597-E611. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00415.2015. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26837808 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Intra-Islet Communication in the Function and Plasticity of the Islets of Langerhans during Health and Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 6;25(7):4070. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074070. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612880 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gilon P, Henquin J. Mechanisms and physiological significance of the cholinergic control of pancreatic beta-cell function. Endocr Rev. 2001;22:565–604. - PubMed
-
- Gautam D, et al. A critical role for beta cell M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in regulating insulin release and blood glucose homeostasis in vivo. Cell Metab. 2006;3:449–461. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B. Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion--implications for health and disease. Diabetologia. 2000;43:393–410. - PubMed
-
- Conn PM, Goodman HM, Kostyo JL. The endocrine system. New York: Published for the American Physiological Society by Oxford University Press; 1998.
-
- Gautam D, et al. Role of the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in beta-cell function and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007;9(Suppl 2):158–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

