Inhibitory effects of calcitriol on the growth of MCF-7 breast cancer xenografts in nude mice: selective modulation of aromatase expression in vivo
- PMID: 21686077
- PMCID: PMC3114631
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-011-0073-7
Inhibitory effects of calcitriol on the growth of MCF-7 breast cancer xenografts in nude mice: selective modulation of aromatase expression in vivo
Abstract
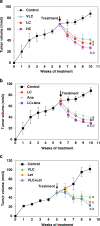
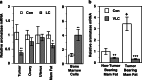
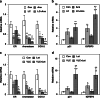
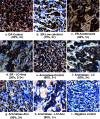
Calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)), the hormonally active metabolite of vitamin D, exerts many anticancer effects in breast cancer (BCa) cells. We have previously shown using cell culture models that calcitriol acts as a selective aromatase modulator (SAM) and inhibits estrogen synthesis and signaling in BCa cells. We have now examined calcitriol effects in vivo on aromatase expression, estrogen signaling, and tumor growth when used alone and in combination with aromatase inhibitors (AIs). In immunocompromised mice bearing MCF-7 xenografts, increasing doses of calcitriol exhibited significant tumor inhibitory effects (~50% to 70% decrease in tumor volume). At the suboptimal doses tested, anastrozole and letrozole also caused significant tumor shrinkage when used individually. Although the combinations of calcitriol and the AIs caused a statistically significant increase in tumor inhibition in comparison to the single agents, the cooperative interaction between these agents appeared to be minimal at the doses tested. Calcitriol decreased aromatase expression in the xenograft tumors. Importantly, calcitriol also acted as a SAM in the mouse, decreasing aromatase expression in the mammary adipose tissue, while increasing it in bone marrow cells and not altering it in the ovaries and uteri. As a result, calcitriol significantly reduced estrogen levels in the xenograft tumors and surrounding breast adipose tissue. In addition, calcitriol inhibited estrogen signaling by decreasing tumor ERα levels. Changes in tumor gene expression revealed the suppressive effects of calcitriol on inflammatory and growth signaling pathways and demonstrated cooperative interactions between calcitriol and AIs to modulate gene expression. We hypothesize that cumulatively these calcitriol actions would contribute to a beneficial effect when calcitriol is combined with an AI in the treatment of BCa.
Keywords: Aromatase; Aromatase inhibitors; Breast cancer; Calcitriol; Estrogen synthesis; Selective aromatase modulator; Xenografts.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

